Medulla Oblongata Collection
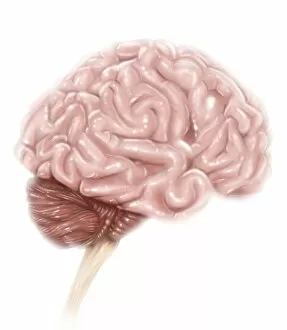
The medulla oblongata, located at the base of the brainstem, is a crucial part of human brain anatomy
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
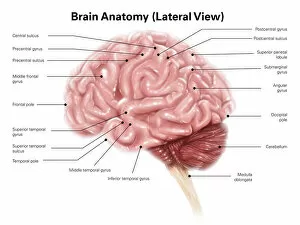
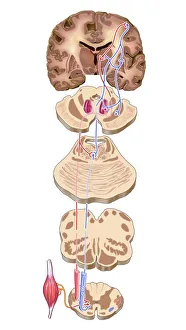
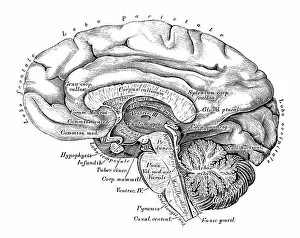
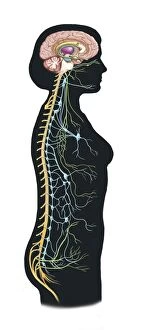
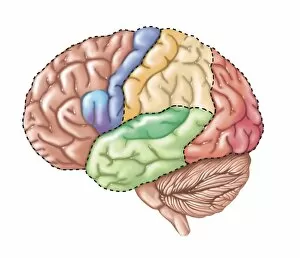
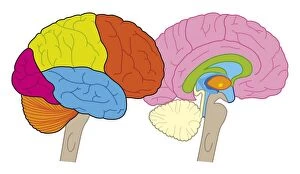
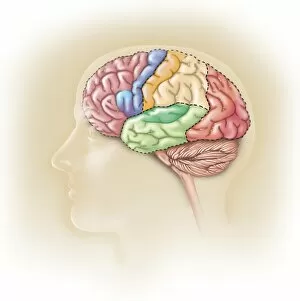
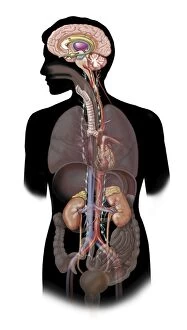
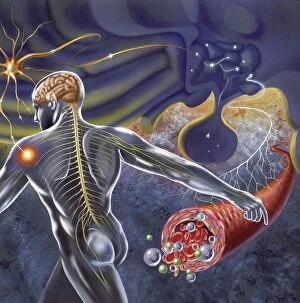
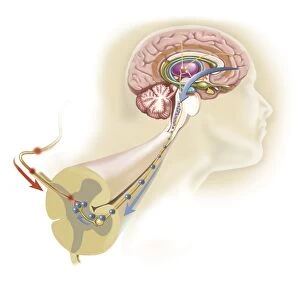
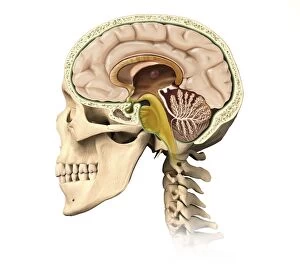
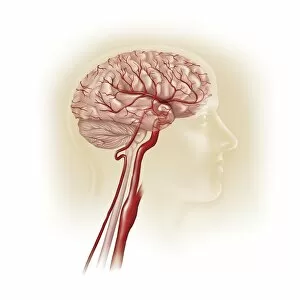
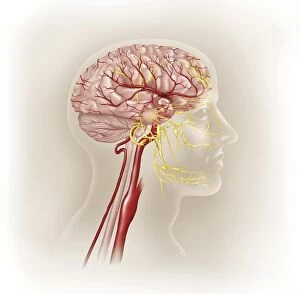
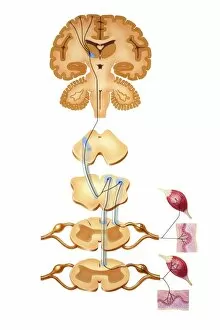
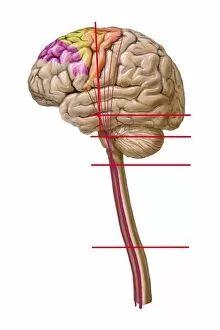
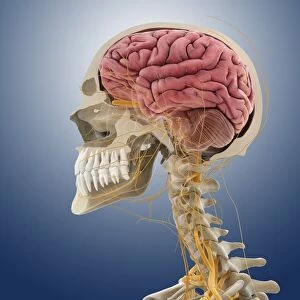
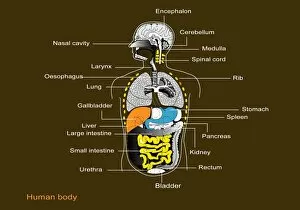
The medulla oblongata, located at the base of the brainstem, is a crucial part of human brain anatomy. In this captivating artwork depicting the lateral view of the brain, we can observe its position and understand its significance in our body's functioning. As we delve deeper into understanding the brain motor cortex pathways, illustrated here as artwork C016 / 6532, we begin to unravel how the medulla oblongata plays a vital role in coordinating our movements. It serves as a bridge between our spinal cord and higher regions of our brain, allowing for seamless communication and control over voluntary actions. Scientific illustrations showcasing various views of human anatomy provide us with valuable insights into how different systems interact within our bodies. The autonomic nervous system and limbic system are highlighted here alongside the medulla oblongata, emphasizing their interconnectedness and influence on essential bodily functions such as breathing, heart rate regulation, and emotional responses. Exploring further surface anatomy reveals functional lobes that contribute to specific cognitive processes. This side view image allows us to appreciate how these lobes work together harmoniously under the guidance of structures like the medulla oblongata. Additionally, it provides an opportunity to marvel at their complexity while acknowledging their importance in shaping who we are as individuals. Intriguingly, even during fetal development depicted through stunning artwork capturing this delicate stage; one can witness early formations of structures like the medulla oblongata taking shape. This emphasizes its fundamental role from early stages onwards in ensuring proper growth and development. Digital illustrations offer a comprehensive overview by highlighting both external features such as lobes while also providing cross-sectional insights into internal structures like sound processing via auditory cortex facilitated by thalamus input through the medulla oblongata. Ultimately, studying brain anatomy leads us to acknowledge that every section has its unique purpose – be it frontal or temporal lobes involved in cognition or occipital lobe responsible for vision.