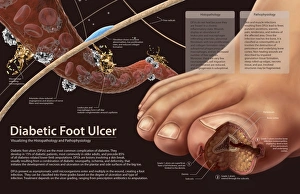
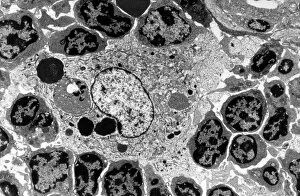
Macrophage Collection
Macrophages, the mighty defenders of our immune system, play a crucial role in protecting us from harmful invaders
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
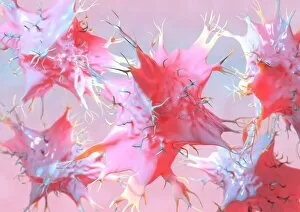
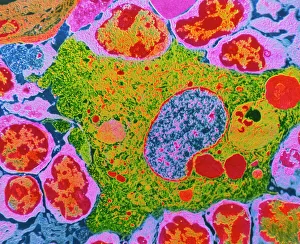
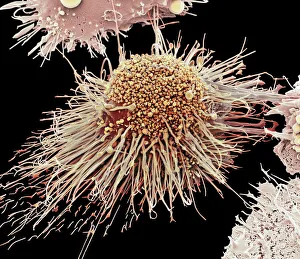
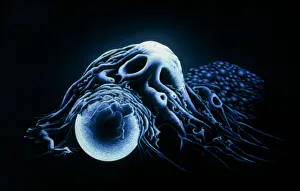
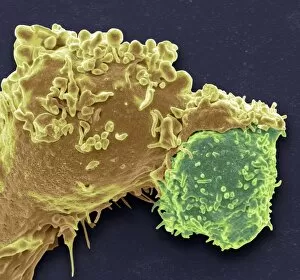
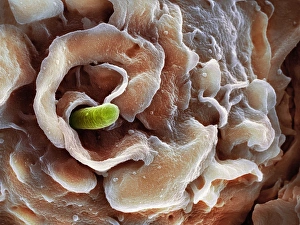
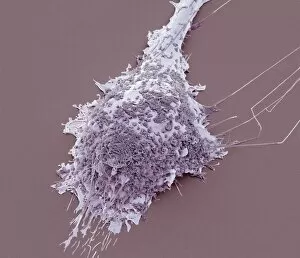
Macrophages, the mighty defenders of our immune system, play a crucial role in protecting us from harmful invaders. These incredible cells are like superheroes, constantly on guard to keep us healthy. In stunning artwork and microscopic images captured by powerful electron microscopes, we get a glimpse into the fascinating world of macrophages. Dendritic cells, another type of immune cell closely related to macrophages, are depicted in beautiful artwork that showcases their intricate structure. A transmission electron microscope (TEM) image reveals the detailed morphology of a human macrophage. Its complex network of cytoplasmic extensions is truly mesmerizing. In another scanning electron microscope (SEM) image, we witness bacteria infecting a macrophage - an intense battle between pathogen and defender. The SEM also captures the moment when a tuberculosis bacterium is engulfed by a determined macrophage. This remarkable act demonstrates how these cells tirelessly eliminate threats within our bodies. An activated macrophage is showcased in yet another SEM image - its surface covered with tiny protrusions called filopodia as it prepares for action against invading pathogens or damaged tissue. But it's not just infectious agents that fall victim to the might of these phagocytic warriors; even non-living objects like beads can be engulfed by them. The versatility and efficiency of macrophages never cease to amaze. Unfortunately, sometimes our own immune system can turn against itself. In multiple sclerosis patients, SEM images reveal abnormalities in myelin-producing cells caused by misguided attacks from malfunctioning immune cells such as macrophages. As we delve deeper into understanding these remarkable guardians of health through TEM images showcasing their cellular structures and functions, we gain valuable insights into how they work tirelessly day and night to keep us safe from harm. From battling bacterial infections to defending against autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis – this captivating journey through various microscopy techniques highlights the extraordinary capabilities possessed by these essential components of our immune system.