Lobe Finned Fish Collection
The lobe-finned fish, also known as Sarcopterygii
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
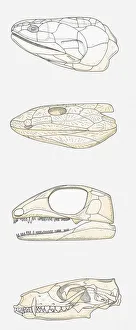
The lobe-finned fish, also known as Sarcopterygii, is a fascinating group of aquatic creatures that have captured the attention of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. These unique fish possess fleshy fins, which resemble limbs and are believed to be an important evolutionary link between fish and land-dwelling animals. In the depths of Africa's wetlands, a majestic Shoebill stork can be seen feasting on a Spotted African lungfish. This incredible sight showcases the intricate balance between predator and prey in nature's grand design. Meanwhile, in ancient times, Metriorhynchus marine reptiles ventured into the waters in search of their next meal – a Coelacanth fish. The struggle for survival played out beneath the waves as these prehistoric creatures fought for dominance. Illustrations bring to life the fin structure of prehistoric lobe-finned fish – showcasing their unique anatomy that set them apart from other species. Alongside these illustrations are depictions of skulls belonging to various vertebrates: fleshy-finned fish (Sarcopterygii), early tetrapods, early reptiles, and mammals. These images provide valuable insights into our understanding of evolution and how different organisms have adapted over time. Underwater scenes reveal two Coelacanth fish gracefully swimming through their watery domain. Their presence reminds us that even amidst modern-day wonders, remnants from ancient times still exist today. An artist's concept takes us on an imaginative journey depicting the evolution from a lobe-finned fish to an amphibian – highlighting how these remarkable creatures paved the way for terrestrial life forms we see today. Delving further back into history reveals Rhizodus - an extinct predatory lobe-finned fish that once roamed Earth's waters with its formidable jaws ready to seize any unsuspecting prey that crossed its path. Lastly, Scaumenacia emerges from the Devonian period as an extinct genus of lobe-finned fish.