Lipids Collection
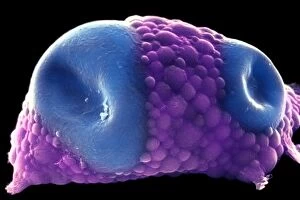
"Lipids: The Building Blocks of Life's Essential Fats" Distended fat cells, as seen in SEM C013 / 5015
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
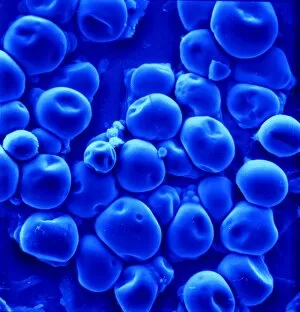
"Lipids: The Building Blocks of Life's Essential Fats" Distended fat cells, as seen in SEM C013 / 5015, reveal the intricate structure and storage capacity within our bodies. In SEM C013 / 5013, distended fat cells showcase the impact of lipid accumulation on overall cell morphology. Witness the mesmerizing high-speed image capturing oil droplets suspended in water - a visual representation of lipids' hydrophobic nature. Behold the polyunsaturated fat molecule - a vital component found in various foods that supports brain health and reduces inflammation. Artistic renderings depict phospholipids forming a protective membrane barrier, showcasing their crucial role in cellular function and structure. Dive into the world of phospholipid molecules through stunning artwork, revealing their unique composition and importance for cell membranes. Explore yet another polyunsaturated fat molecule, highlighting its significance as an essential nutrient for maintaining heart health and promoting proper bodily functions. Immerse yourself in captivating artwork depicting intricate layers of adipose tissue - illustrating how they can stored within our bodies to provide energy reserves and insulation. Discover the intricately designed intestinal villi through artistic interpretation, emphasizing how lipids aid in nutrient absorption during digestion processes. Delve into Leydig cells with a light micrograph (C016 / 0520), shedding light on their role in producing hormones such as testosterone from cholesterol-derived precursors – showcasing another aspect of lipid functionality beyond energy storage alone. Sugar crystals captured under a microscope (C014 / 2643) remind us that not all fats are created equal; understanding different types is crucial for maintaining balanced nutrition choices. Witness once again oil droplets suspended gracefully amidst water - this high-speed image serves as a reminder that even at microscopic levels, lipids play a significant role in various natural phenomena.