Ischemia Collection
Ischemia, also known as Ischaemia, is a medical condition that occurs when there is an inadequate blood supply to a specific organ or part of the body
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
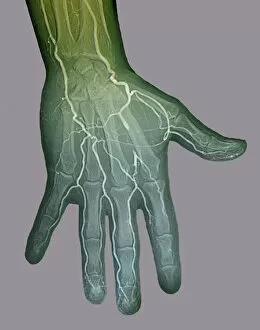
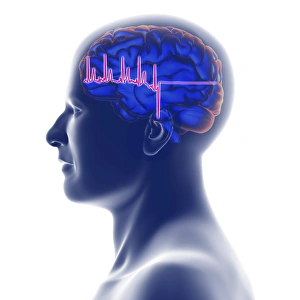
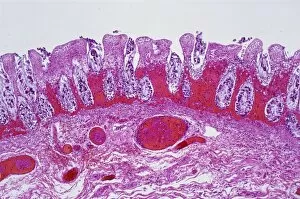
Ischemia, also known as Ischaemia, is a medical condition that occurs when there is an inadequate blood supply to a specific organ or part of the body. This caption explores various diagnostic techniques and artistic representations related to ischemia. Starting with digital angiogram images, we can observe the intricate network of blood vessels affected by ischemia. The ECG trace alongside an MRI brain scan showcases the impact on neurological health, highlighting the importance of early detection and treatment. Artwork depicting an ECG trace superimposed on a head with a brain symbolizes the connection between cardiovascular health and brain function. It serves as a reminder that ischemic events can have severe consequences for cognitive abilities. Further emphasizing this point, another artwork combines an ECG trace with multiple MRI brain scans. These visual representations demonstrate how they are lead to strokes, which are depicted in detailed artwork showcasing their devastating effects (Stroke, artwork F006 / 7915). Moving beyond strokes, light micrographs reveal the damage caused by ischemic bowel - yet another manifestation of this condition affecting different organs. A striking MRI scan unveils a berry aneurysm associated with ischemia; its presence highlights potential risks and complications that need attention. Lastly, CT scans provide additional insights into stroke cases linked to ischemia. These images serve as valuable diagnostic tools for healthcare professionals in identifying and assessing patients' conditions accurately. In summary, these diverse visuals shed light on different aspects – from its impact on cerebral health through strokes to its effects on other vital organs like bowels. They emphasize the significance of timely diagnosis using advanced imaging techniques such as digital angiograms or MRI/CT scans while reminding us about the urgent need for preventive measures against this potentially debilitating condition.