Hominini Collection
"Hominini: Unveiling the Evolutionary Journey of Humanity" Step into the fascinating world of Hominini, a diverse group of primates that includes our ancient ancestors
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
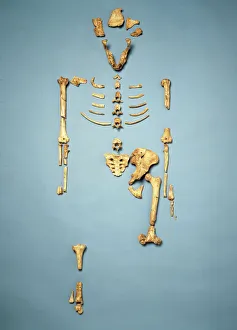
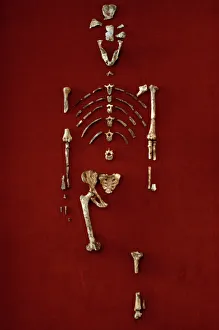
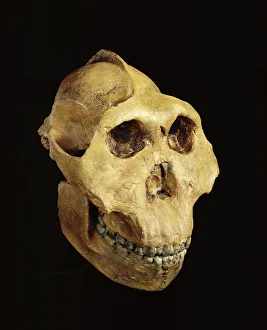
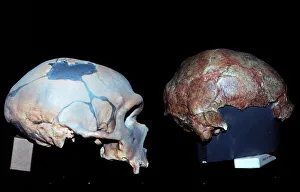
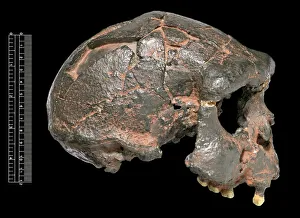
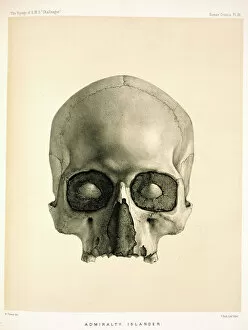
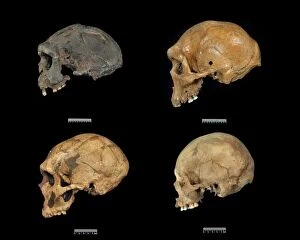
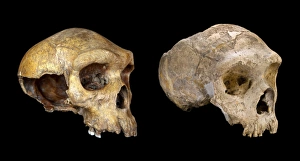
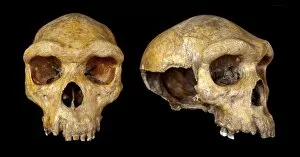
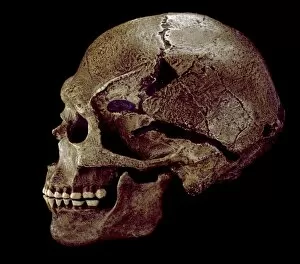
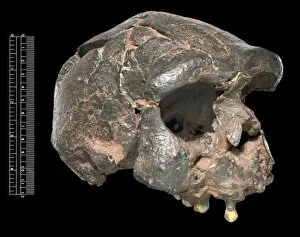
"Hominini: Unveiling the Evolutionary Journey of Humanity" Step into the fascinating world of Hominini, a diverse group of primates that includes our ancient ancestors. From the sensory homunculus mapping our intricate neural pathways to the hominid crania revealing clues about their intelligence and culture, each discovery paints a vivid picture of our evolutionary past. Meet Australopithecus afarensis (AL 288-1), affectionately known as Lucy, whose fossilized remains provide crucial insights into early human bipedalism. As we explore further, we encounter Homo erectus (Sangiran 17) and ponder their migration out of Africa, paving the way for Homo sapiens and Neanderthals. The motor homunculus showcases how different areas in our brain control specific body movements while Homo neanderthalensis demonstrates their prowess with a Neanderthal spear point at Swanscombe, UK. Meanwhile, Paranthropus boisei (Zinjanthropus) cranium (OH5) offers glimpses into an extinct branch diverging from our own lineage. Delving deeper still, we uncover intriguing artifacts like The Makapansgat Pebble—a remarkable example of early symbolic thinking—and marvel at the complexity within us all. From the liver's vital role in metabolism to studying human cells under a microscope, every aspect contributes to understanding what it means to be human. As we piece together this mosaic of humanity's story through time and space, one thing becomes clear: Hominini is not just an exploration but also an appreciation for how far we have come. Let us embrace this journey with curiosity and awe as we continue unraveling the mysteries that connect us all.