Heparin Collection
Heparin: Unveiling the Intricate Dance of Basophils and Mast Cells In the intricate world of our immune system
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
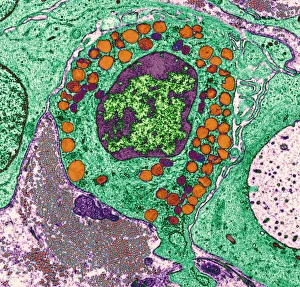
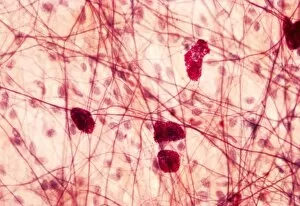
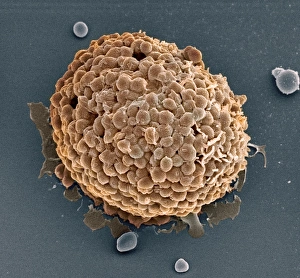
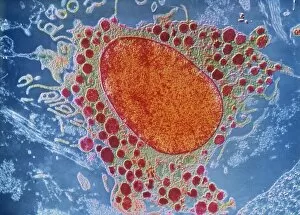
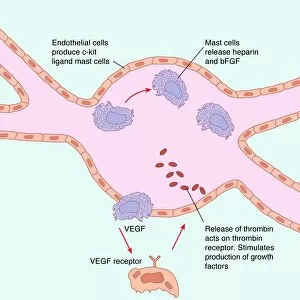
Heparin: Unveiling the Intricate Dance of Basophils and Mast Cells In the intricate world of our immune system, heparin plays a crucial role in regulating allergic reactions. This 150-word caption explores the fascinating connection between basophil white blood cells and mast cells, shedding light on their interplay during an allergic response. Conceptual images depict mast cells releasing histamine due to an allergic reaction, showcasing their pivotal role in triggering inflammatory responses. These microscopic powerhouses are captured through both light micrographs and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), revealing their intricate structures. Basophil white blood cells also take center stage as they interact with mast cells to orchestrate immune responses. TEM images provide a closer look at these enigmatic defenders, highlighting their unique features and mechanisms. Together, basophils and mast cells form a dynamic duo that safeguards our bodies against harmful invaders but can sometimes misfire during allergies. Heparin acts as a regulator in this dance by inhibiting clotting factors released by basophils and preventing excessive inflammation caused by histamine release from mast cells. Understanding heparin's vital role in modulating these cellular interactions brings us one step closer to unraveling the complexities of our immune system's defense strategies.