Genetic Modification Collection
"Exploring the Boundaries of Nature: Genetic Modification Unveiled" A mesmerizing illustration showcases the fascinating Splake
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
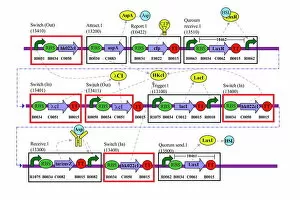
"Exploring the Boundaries of Nature: Genetic Modification Unveiled" A mesmerizing illustration showcases the fascinating Splake, a hybrid fish resulting from crossing female lake trout and male brook trout – a testament to genetic modification's potential. Ever wondered about square tomatoes? Genetic modification has paved the way for these intriguing creations that challenge conventional shapes and redefine our perception of nature's bounty. Dive into the intricate world of genetic circuits with a captivating diagram, unraveling how scientists manipulate genes to unlock new possibilities in medicine, agriculture, and beyond. Witness the power of nature as a woman proudly displays her roots – not just metaphorically but literally. Genetic modification allows us to explore our heritage in ways we never thought possible. Behold the stunning Abutilon flower, an exquisite example of how they are enhance beauty and create breathtaking variations within plant species. Step into the future as a robot delicately injects life-altering modifications into organisms – showcasing humanity's quest to harness genetics for innovation and progress. In Iowa, USA, witness a corn seedling sprouting from a test tube against contrasting backgrounds - reminding us how genetic modification is revolutionizing crop development for sustainable farming practices. Uncover an eerie scene where grey aliens awaken humanoid clones inside bio-transport containers - provoking contemplation on ethical dilemmas surrounding extreme applications of genetic engineering. Immerse yourself in springtime bliss with vibrant crocus hybrids blooming across meadows; these genetically modified wonders bring forth colors that were once unimaginable in nature. Reflect on cautionary tales as you encounter an evocative conceptual image portraying GM gone wrong – urging responsible scientific exploration while acknowledging potential risks associated with tampering with genes. 11 (repeated). Return to Iowa's laboratories where another corn seedling emerges from its sterile environment; this time against a white background - symbolizing the ongoing pursuit of knowledge and innovation through genetic modification.