Genetic Material Collection
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Genetic Material: From Chloroplast Structure to Paramyxovirus Particles" Genetic material, the blueprint of life
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
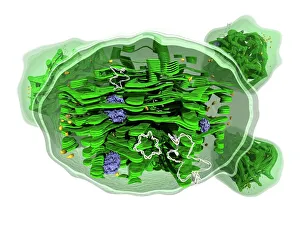
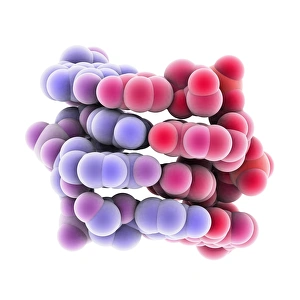
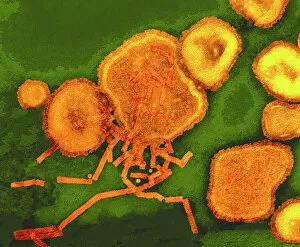
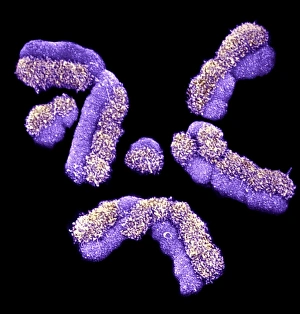
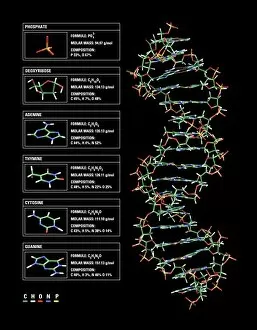
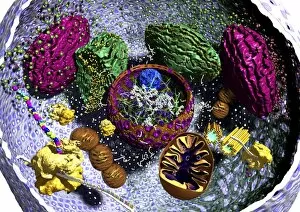
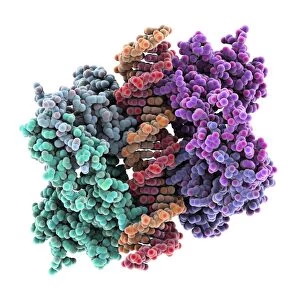
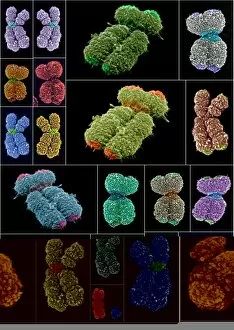
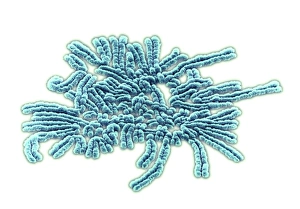
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Genetic Material: From Chloroplast Structure to Paramyxovirus Particles" Genetic material, the blueprint of life, is a captivating realm that holds the secrets to our existence. Within this enigmatic domain lies an array of awe-inspiring elements, each playing a crucial role in shaping who we are. Gazing at the intricate chloroplast structure, one cannot help but marvel at its elegance. Like tiny green factories within plant cells, these structures harness sunlight and convert it into energy through photosynthesis. They hold the key to sustaining life on Earth by producing oxygen and nourishing countless organisms. Zooming in further, we encounter the Z-DNA tetramer molecule C015/6557 - a mesmerizing sight indeed. This unique DNA conformation challenges conventional wisdom with its left-handed helix shape. It serves as a reminder that nature's creativity knows no bounds when it comes to genetic diversity. Moving along our journey through genetic wonders, we stumble upon chromosomes - nature's organized libraries of information. These compact bundles carry genes responsible for inherited traits and play an essential role in cell division and growth. Peering through powerful microscopes reveals another breathtaking spectacle: paramyxovirus particles captured using TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy). These minuscule entities are notorious for causing respiratory infections in humans but also serve as valuable tools for scientific research. Shifting gears from viruses to human chromosomes brings us face-to-face with SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) images showcasing their intricate details. Each chromosome carries an individual's unique genetic code, determining everything from eye color to susceptibility to diseases – truly remarkable. As we delve deeper into cellular landscapes, eukaryotic cells unveil their interior splendor. Here lies where all genetic material resides; a bustling hub where DNA molecules orchestrate life's symphony with precision and finesse. Artistic renditions of DNA molecules adorn our path like masterpieces in a gallery.