Fibrils Collection
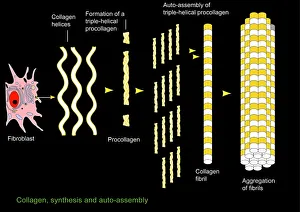
"Fibrils: Unveiling the Intricate Web of Collagen Synthesis and Assembly" Collagen synthesis and assembly form the foundation of fibril formation
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
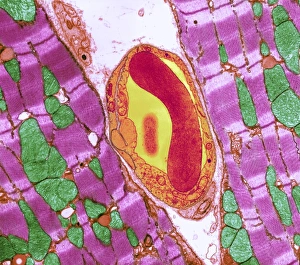
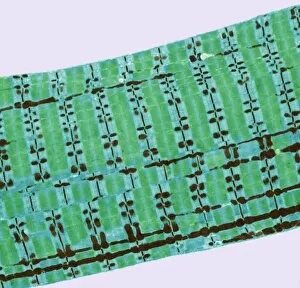
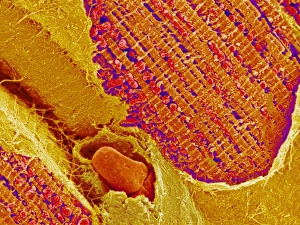
"Fibrils: Unveiling the Intricate Web of Collagen Synthesis and Assembly" Collagen synthesis and assembly form the foundation of fibril formation, as depicted in this captivating artwork. These microscopic structures play a vital role in various biological processes, including cardiac muscle function. In a stunning transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image, we witness the intricate connection between cardiac muscle fibers and capillaries. This close interaction ensures efficient oxygen supply to sustain the demanding workload of the heart. Delving deeper into sugar uptake within muscles, a detailed diagram illustrates how essential nutrients are transported to fuel muscular activity. The complexity behind this process becomes apparent as we explore its intricacies. Shifting our focus to nature's wonders, an algae cell wall is beautifully captured using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The fibrous composition of this structure showcases nature's ability to create robust yet flexible barriers for protection and support. Examining human muscle fibers through a comprehensive diagram reveals their organized arrangement. Each fiber contributes to overall strength and movement capabilities while highlighting their unique characteristics within different types of muscles. Returning to TEM imagery, we once again observe the harmonious relationship between cardiac muscle cells and capillaries. This interplay highlights how these specialized cells work together seamlessly for optimal heart performance. Zooming even closer with SEM technology, we gain insight into the intricate details that make up cardiac muscle tissue itself. Its distinct pattern emphasizes both its strength and flexibility—essential qualities for maintaining proper heart function. Cardiac muscles stand out due to their remarkable abilities; they tirelessly contract without fatigue throughout our lives. TEM images capture their structural elegance while reminding us of their crucial role in sustaining life-sustaining circulation. Expanding our exploration further, skeletal muscles come into view through TEM imaging—revealing another level of complexity within striated fibers responsible for voluntary movements such as walking or lifting weights. Once more utilizing SEM techniques on cardiac muscles allows us to appreciate their three-dimensional architecture.