Epithelia Collection
Epithelia, the microscopic heroes of our body's defense system
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
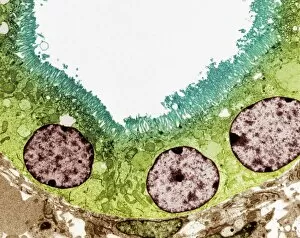
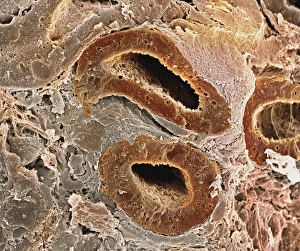
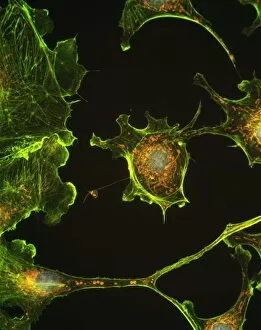
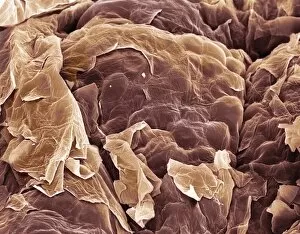
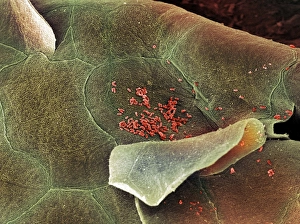
Epithelia, the microscopic heroes of our body's defense system. 🌟 From the bacteria-fighting warriors in our nose to the intricate structures within our organs, epithelial cells play a vital role in maintaining our health. Let's take a closer look at these fascinating entities through various scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM) images. In one captivating SEM image, we observe bacteria residing on the surface of nasal epithelial cells. These tiny organisms are met with fierce resistance from these specialized cells, which act as guardians against invading pathogens. Shifting focus to another SEM capture, we explore the gallbladder surface. The highly detailed C015/9613 image showcases its unique architecture, revealing an intricate network of epithelial cells that line this organ. Their arrangement ensures efficient bile storage and release for digestion purposes. Continuing our exploration of gallbladder surfaces through SEM imagery, we encounter two more stunning captures labeled C015/9611 and C015/9612. These visuals provide further insight into the delicate structure of epithelial cells found here – their interconnections forming a protective barrier while facilitating essential functions. Moving deeper into our internal systems using TEM imaging techniques, we delve into kidney tubules' microscopic world. Two TEM images showcase these intricate structures responsible for filtering waste products from blood while reabsorbing valuable substances like water and electrolytes. TEM also allows us to zoom in on cell nuclei – command centers orchestrating cellular activities. A striking TEM visualization presents us with this central hub brimming with genetic information inside a kidney tubule cell nucleus. Stepping away from kidneys but staying within reproductive anatomy territory, an intriguing SEM image reveals fallopian tube epithelium. This delicate tissue plays a crucial role in guiding eggs towards fertilization sites within the female reproductive system. Returning to TEM imaging once again brings us face-to-face with another glimpse into cell nuclei; this time observed within nasal epithelial cells.