Endoplasmic Reticulum Collection
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex network of membranes found in eukaryotic cells and can be divided into two main types
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
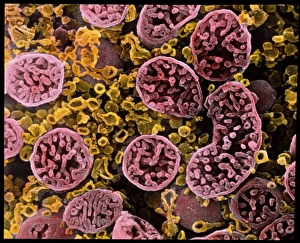
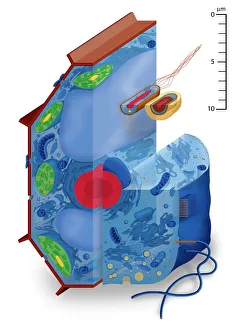
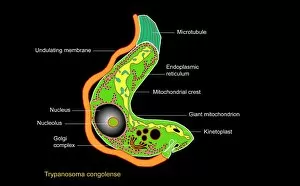
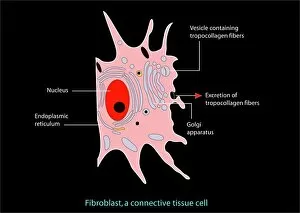
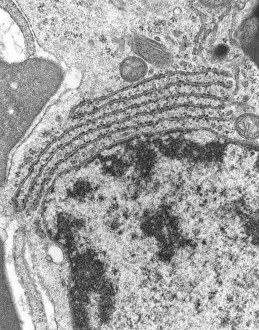
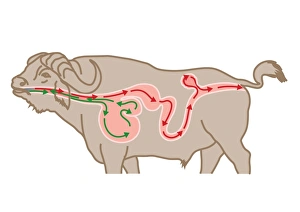
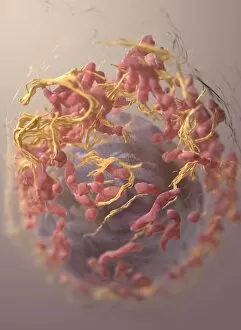
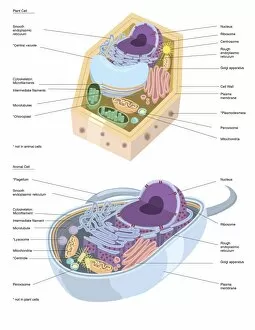
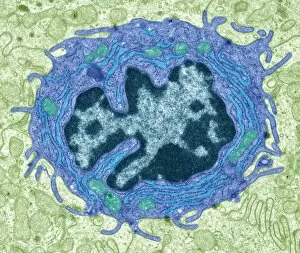
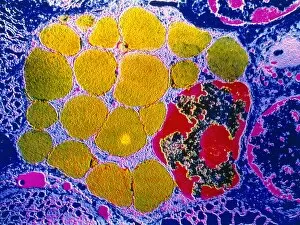
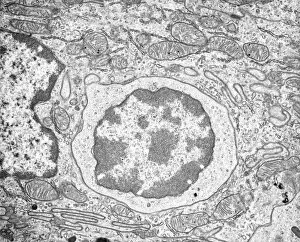
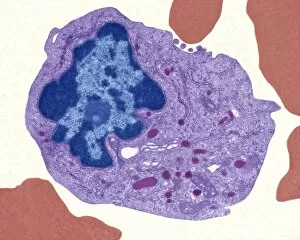
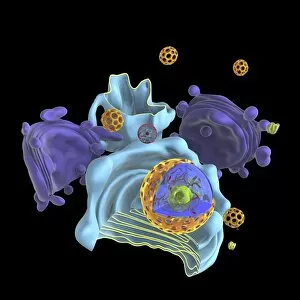
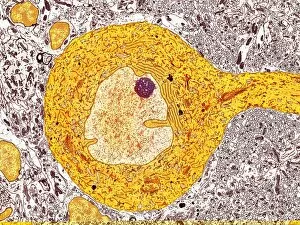
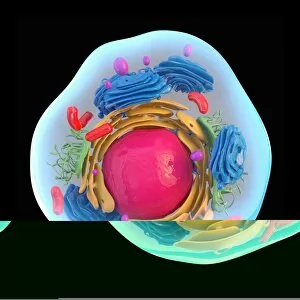
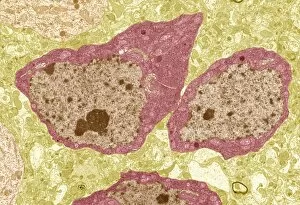
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex network of membranes found in eukaryotic cells and can be divided into two main types: rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The RER is studded with ribosomes, giving it a rough appearance under the transmission electron microscope (TEM). In contrast, the SER lacks ribosomes and appears smooth. One fascinating aspect of the ER is its involvement in various cellular processes. For instance, TEM images reveal coloured scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of mitochondria in ovarian cells, highlighting their close association with the ER. Different cell types also showcase unique artwork representations, such as trypanosome protozoan or Purkinje nerve cell. Artwork depicting fibroblast cells emphasizes their role in tissue repair and collagen production. Understanding animal cell structure becomes easier when observing hepatocyte liver cells through TEM or skin cancer cells via SEM. Cross-section illustrations provide insights into human cell organization while digital cross-sections illustrate the four chambers of a ruminant's stomach, including rumen and reticulum compartments. Lastly, conceptual images help visualize plant cell components like chloroplasts and vacuoles. Exploring the world offers a glimpse into cellular intricacies across different organisms and tissues.