Endocardium Collection
The endocardium, the innermost layer of the heart, plays a crucial role in maintaining proper cardiac function
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
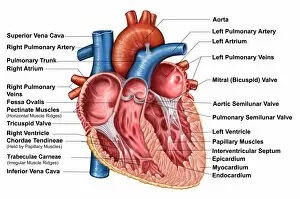
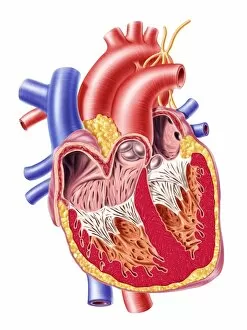
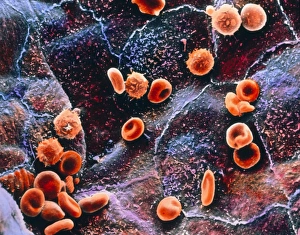
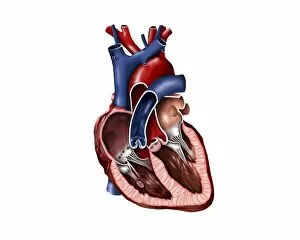
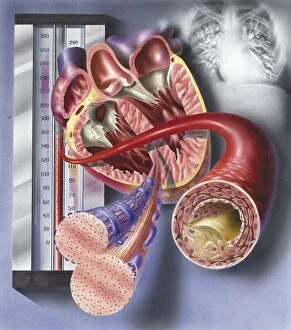
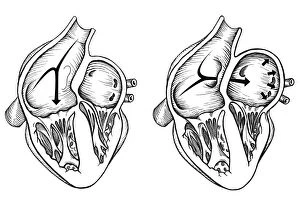
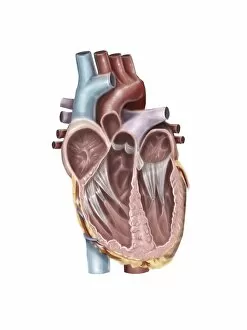
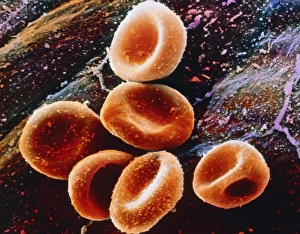
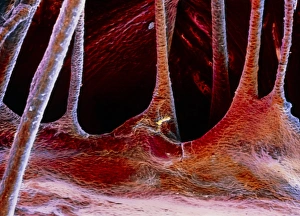
The endocardium, the innermost layer of the heart, plays a crucial role in maintaining proper cardiac function. In this captivating image, taken from a frontal section of the human heart, we get an intimate glimpse into its intricate anatomy. Using false-colour scanning electron microscopy (SEM), blood cells can be seen gracefully gliding along the surface of the endocardium. This mesmerizing view not only showcases its smoothness but also highlights its vital role in facilitating efficient blood flow. Moving to a cross-section of the human heart, we witness another remarkable sight – an internal view that reveals both atria and ventricles. The endocardium is clearly visible here as it lines these chambers with delicate precision. Zooming further into this cross-section, our attention is drawn to muscle cells and an atherosclerotic artery. This detailed close-up sheds light on how the endocardium interacts with other components within the heart and emphasizes its importance in maintaining cardiovascular health. Heart valves take center stage in another captivating image featuring pulmonary valve, mitral valve, and tricuspid valve. These structures are intimately connected to the endocardium and work harmoniously to ensure unidirectional blood flow throughout each heartbeat. A comparison between a normal heart and one with a patent foramen ovale provides valuable insights into how variations in endocardial structure can impact cardiac function. Understanding such differences allows us to better comprehend various cardiovascular conditions. Finally, we encounter an enlarged left ventricle – yet another testament to the significance of studying endocardial health. By exploring these interior views of our most vital organ, we gain invaluable knowledge about its complex workings and potential abnormalities that may arise. Delving deep into images showcasing different aspects offers us glimpses into both beauty and complexity within our own bodies. It serves as a reminder that understanding this essential component is key to unraveling mysteries surrounding cardiac health.