Encode Collection
"Unlocking the Secrets: The Fascinating World of Encode" Delving into the intricate world of genetics
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
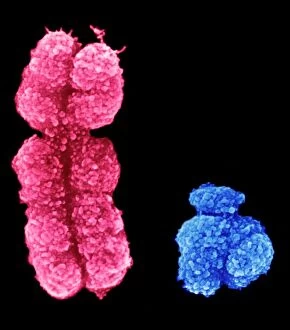
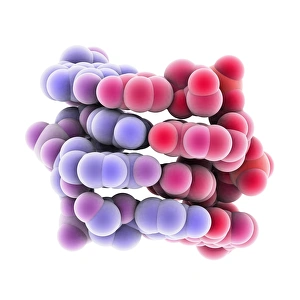
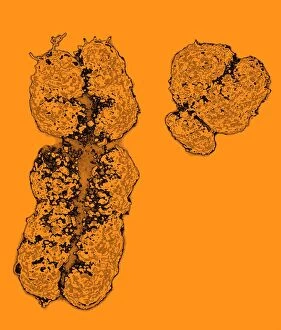
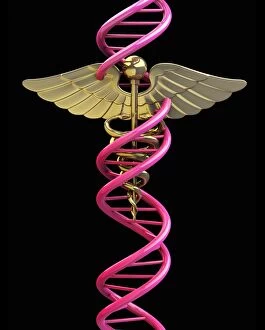
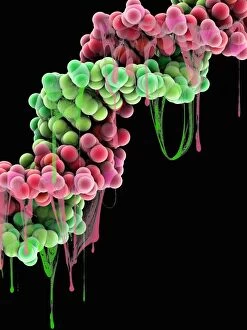
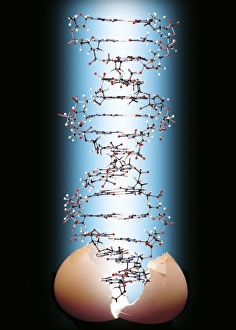
"Unlocking the Secrets: The Fascinating World of Encode" Delving into the intricate world of genetics, Encode takes us on a journey through the enigmatic realm of encoding. At its core lies the DNA molecule, an extraordinary blueprint that encodes life itself. In our exploration, we encounter mesmerizing abstract images depicting the DNA molecule's complexity and beauty. Like an artwork crafted by nature, it captivates with its elegant structure and holds within it the key to our existence. Zooming in further, we discover Z-DNA tetramer molecule C015 / 6557 - a fascinating glimpse into the building blocks that shape our genetic makeup. It unravels mysteries hidden within those X and Y chromosomes, defining who we are as individuals. As we travel through time, history reveals how encoding has extended beyond biology. U. S. Troops learning cryptography in Tarawa during June 1943 showcases how this art transcends boundaries – from deciphering military secrets to safeguarding information crucial for national security. Stepping back even further into history, we encounter A Jacquard Loom from 1915 - a pioneering invention that revolutionized textile production by utilizing punch cards for encoding patterns. This early example demonstrates how humans have long sought ways to encode information efficiently. Art intertwines with science as Caduceus with DNA comes alive before our eyes - a stunning representation merging ancient symbolism with modern understanding. It reminds us that decoding life's intricacies requires both scientific knowledge and artistic interpretation. Encode brings forth an appreciation for these remarkable codes embedded within every living being. From DNA molecules delicately weaving together to form complex organisms to encrypted messages safeguarded throughout history – encoding is truly at the heart of humanity's quest for knowledge and understanding.