Electron Micrograph Collection
"Unlocking the Hidden World: Exploring Electron Micrographs" Delve into the microscopic realm and witness the intricate beauty of life through electron micrographs
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
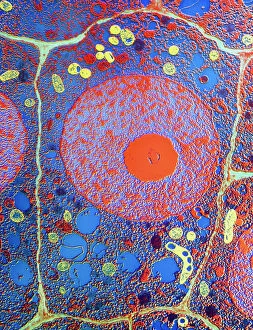
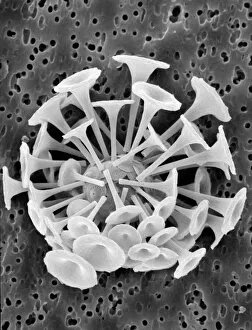
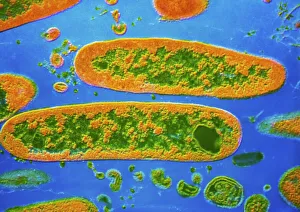
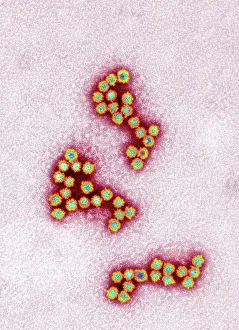
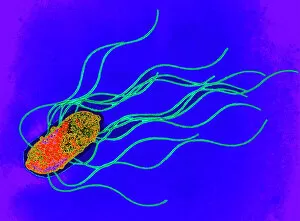
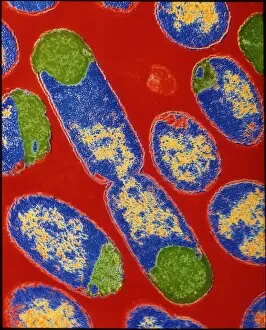
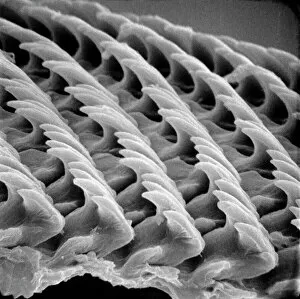
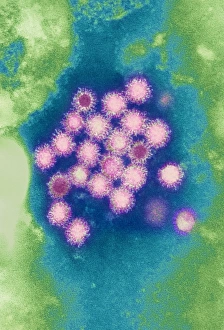
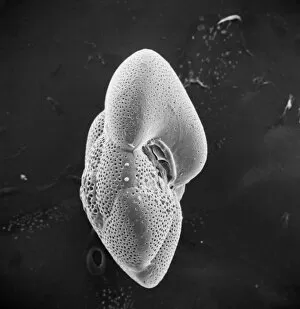
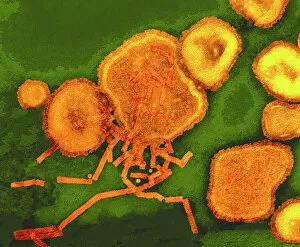
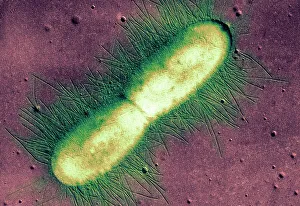
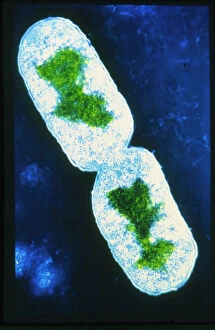
"Unlocking the Hidden World: Exploring Electron Micrographs" Delve into the microscopic realm and witness the intricate beauty of life through electron micrographs. Discosphaera tubifera, coccolithophore: Marvel at the stunning calcium carbonate plates adorning this marine phytoplankton, resembling a delicate work of art. Crysotile asbestos: Peer into the dangerous fibers that make up this mineral, revealing its hazardous nature when inhaled. Liver: Journey inside this vital organ and observe its complex network of cells, unveiling its role in detoxification and metabolism. Cimex lectularius, bed bug: Get up close with these notorious pests as their exoskeletons reveal their resilience to survive even against our best efforts. Coloured TEM of Yersinia pestis bacteria: Witness the haunting beauty of these deadly bacteria responsible for causing plague outbreaks throughout history. Taraxacum officinale, dandelion (fruiting head): Explore the intricate structure of a dandelion's fruiting head under high magnification, showcasing nature's ingenious method for seed dispersal. Simulium damnosum, Simulian blackfly: Encounter these tiny insects known for transmitting river blindness as you uncover their detailed anatomy and feeding mechanisms. Norovirus particles, TEM: Enter the world of viruses as you observe norovirus particles - a common cause of gastrointestinal illness - providing insights into their structure and potential vulnerabilities for future treatments. 9 & 10 E. coli bacterium/bacteria : Dive deep into both individual E. coli cells or colonies to understand their role in digestion while also highlighting concerns surrounding foodborne illnesses caused by certain strains. Snail teeth : Discover how snails possess an unexpected weapon – razor-sharp teeth – enabling them to feed on tough plant material with ease; an evolutionary marvel. Chloroplast in cell of pea plant.