Dopamine Collection
Dopamine: Unraveling the Intricacies of a Neurotransmitter Schizophrenia, ecstasy, and Parkinson's disease may seem unrelated at first glance
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
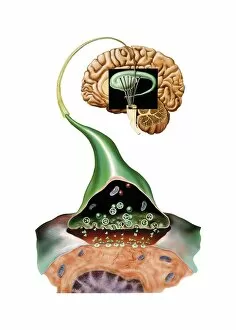
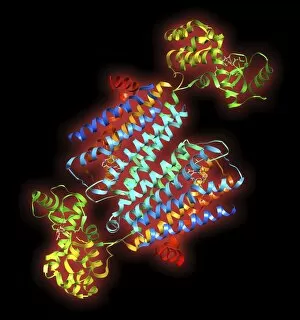
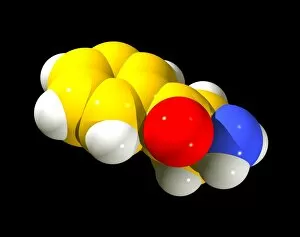
Dopamine: Unraveling the Intricacies of a Neurotransmitter Schizophrenia, ecstasy, and Parkinson's disease may seem unrelated at first glance, but they all share a common thread - dopamine. As one of the key neurotransmitters in our brain, dopamine plays a crucial role in various aspects of our mental and physical well-being. At its core, a molecule that acts as a messenger between neurons. It carries signals across synapses, facilitating communication within the brain. However, an imbalance or dysfunction in this neurotransmitter can lead to profound effects on our mental health. In schizophrenia, researchers have found abnormalities in dopamine signaling pathways. This discovery has shed light on potential treatments for this complex disorder by targeting specific dopamine receptors such as Dopamine receptor D3 C016 / 4464. The recreational drug ecstasy also impacts dopamine levels in the brain. Its euphoric effects are believed to be linked to increased release and inhibition of reuptake of this neurotransmitter. However, prolonged use can disrupt normal functioning and result in long-term changes to the brain's reward system. A digital illustration showcasing the direction flow highlights its involvement with essential regions like the nucleus accumbens, basal ganglia, and ventral tegmental area within the human brain. These areas are intricately connected and play vital roles in motivation, pleasure-seeking behavior, addiction processes, and movement control respectively. On another note, Dopamine molecules take center stage multiple times throughout these discussions due to their significance. The Domperidone anti-sickness drug molecule is one example where it interacts with specific receptors to alleviate nausea symptoms by modulating dopaminergic activity. Moreover, the Levodopa Parkinson's disease drug utilizes levodopa, a precursor for dopamine, to replenish depleted stores. This medication helps manage motor symptoms associated with Parkinson's disease by increasing available levels of this critical neurotransmitter. As we continue unraveling the complexities surrounding dopamine, we gain a deeper understanding of its impact on our brain and behavior.