Diabetes Collection (page 3)
"Unveiling the Complexities of Diabetes: From Insulin Crystals to Groundbreaking Discoveries" In a mesmerizing light micrograph C017 / 8249
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
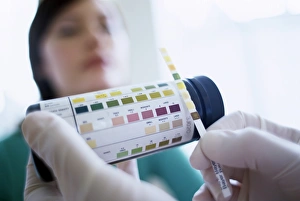
"Unveiling the Complexities of Diabetes: From Insulin Crystals to Groundbreaking Discoveries" In a mesmerizing light micrograph C017 / 8249, insulin crystals shimmer like tiny diamonds, representing hope for millions battling diabetes. These microscopic wonders hold the key to regulating blood sugar levels and transforming lives. Januvia diabetes drug molecule emerges as a game-changer in the fight against this chronic condition. Its molecular structure symbolizes progress and innovation, offering new possibilities for managing diabetes with greater precision. Testing urine glucose levels becomes an essential ritual for those living with diabetes. This simple yet crucial test acts as a compass, guiding individuals towards maintaining optimal health and making informed decisions about their well-being. Advertisements for patent medicines from 1899 transport us back in time when remedies were sought far and wide. Among them, Apollinaire Bouchardat's French trade card promoting Brusson Jeunes gluten bread stands out as a beacon of hope for those seeking relief from diabetes symptoms. Alterations et lesions organiques à la dernière période du diabète showcases the intricate pathophysiology of this condition through vibrant color lithographs. It serves as a reminder that understanding these complexities is vital in providing effective treatments and support to patients. Thomas Willis, an esteemed English physician from the 17th century depicted by George Vertue in 1742, laid foundations for our comprehension of diabetes. His contributions paved the way for future medical advancements that continue to shape our understanding today. Frederick Grant Banting's portrait captures his groundbreaking work on insulin discovery in 1923—a breakthrough that revolutionized diabetic care worldwide. This Canadian physiologist's dedication continues to inspire researchers striving towards improved treatments and ultimately finding a cure. A diagram dating back to 1883 offers insight into early attempts at unraveling the mysteries surrounding diabetes—an invaluable piece of history reminding us how far we have come on this journey towards better management and prevention.