Cosmology Collection
"Unlocking the Mysteries of the Universe
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
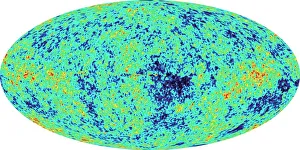
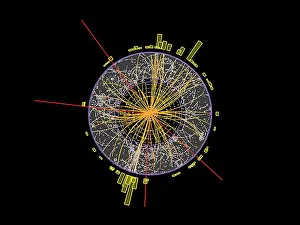
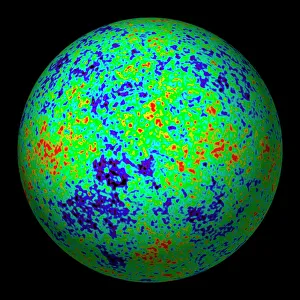
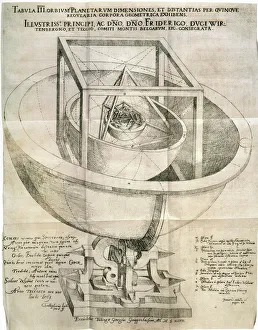
"Unlocking the Mysteries of the Universe: A Journey through Cosmology" Step into the vastness of space and embark on a cosmic adventure as we delve into the captivating realm of cosmology. From iconic images like the Hubble Ultra Deep Field 2012, where thousands of galaxies shimmer in an awe-inspiring tapestry, to witnessing celestial events like the 1919 solar eclipse that revolutionized our understanding of gravity. The Hubble Space Telescope's view of nebula NGC 604 transports us to a mesmerizing world filled with swirling gases and stellar nurseries, reminding us that amidst this grandeur lies the birthplace of stars. The Flammarion engraving takes us even further back in time, capturing humanity's eternal fascination with reaching beyond our earthly confines. Gazing up at night sky wonders such as The Plough asterism in Ursa Major or Orions belt, we are reminded that these constellations have guided explorers for centuries. And it is through instruments like the Hubble Ultra Deep Field galaxies image or MAP microwave background data that we uncover secrets hidden within distant corners of our universe. Marvel at nature's artistic prowess showcased by phenomena such as Pillars of Creation and gas pillars in the Eagle Nebula – towering structures sculpted by cosmic forces over millennia. Even medieval artwork depicting celestial mechanics reveals how ancient minds sought to comprehend Earth's place among heavenly bodies. Cosmology invites us to ponder profound questions about existence itself – from unraveling mysteries surrounding dark matter and energy to exploring theories about parallel universes. It beckons both scientists and dreamers alike to push boundaries, expand knowledge, and embrace humanity's insatiable curiosity about what lies beyond L atmosphere. In this ever-evolving field, each discovery fuels our collective quest for understanding while igniting wonderment within ourselves. So let us journey together through this captivating cosmos; its beauty knows no bounds and its secrets are waiting to be unveiled.