Cortex Collection
The cortex, a fascinating part of the brain, is responsible for numerous functions that are essential to our daily lives
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
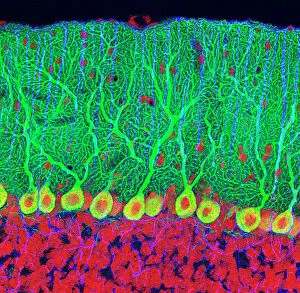
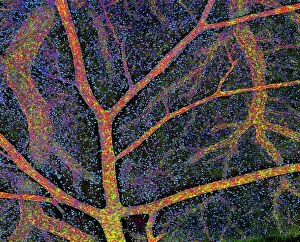
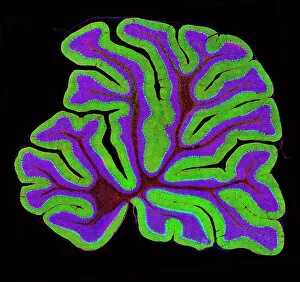
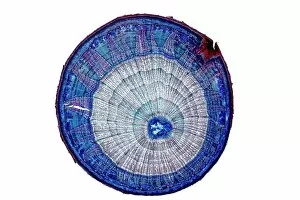
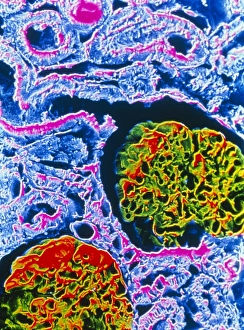
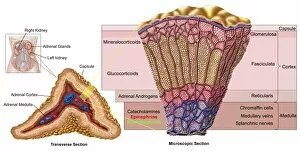
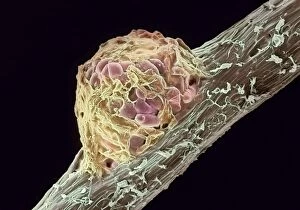
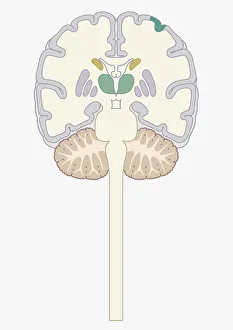
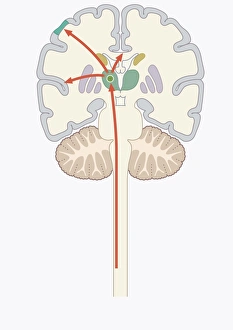
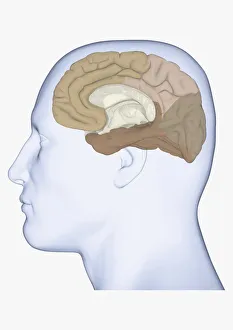
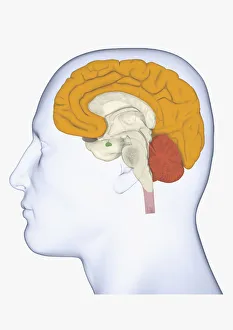
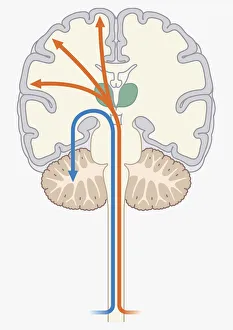
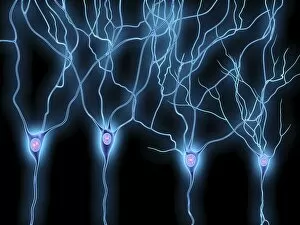
The cortex, a fascinating part of the brain, is responsible for numerous functions that are essential to our daily lives. One remarkable aspect of the the motor homunculus, a representation of how different parts of our body are controlled by specific areas in the brain. This intricate map showcases the complexity and precision with which movements are coordinated. Purkinje nerve cells in the cerebellum play a crucial role in maintaining balance and coordination. These unique cells have an elaborate branching structure that allows them to transmit information efficiently within this important region of the brain. Examining a vascular bundle under scanning electron microscopy reveals its intricate network, highlighting how blood vessels supply vital nutrients and oxygen to sustain healthy brain tissue. Artwork depicting basal ganglia captures their significance as they contribute to various functions such as movement regulation and decision-making processes. Their interconnectedness emphasizes their influence on overall brain function. Understanding the complex system that ensures proper blood supply to brain tissue is crucial. The delicate balance between oxygen delivery and demand plays a critical role in maintaining optimal cognitive function. A light micrograph showcasing a lime tree stem provides insight into plant anatomy but also serves as a reminder of nature's intricate design parallels with human biology. Similar Purkinje nerve cells can be found within the cerebellum structure when observed under light microscopy. Their distinct appearance further emphasizes their importance in coordinating movements smoothly and precisely. Phantom pain after amputation remains an enigma; artwork capturing this phenomenon highlights its impact on individuals who experience sensations from missing limbs—an intriguing area where neuroscience continues to seek answers. Exploring water fern rhizome under light microscopy offers glimpses into its internal structures, reminding us that biological intricacies extend beyond humans alone—a testament to nature's diversity and complexity. A pine tree stem captured through light microscopy unveils its cellular composition—underscoring similarities between plant tissues and those found within our own bodies—a reflection of shared evolutionary history across species boundaries.