Coccus Collection
"Coccus: A Microscopic World Unveiled" In the realm of microbiology, coccus-shaped organisms have captivated scientists for centuries
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
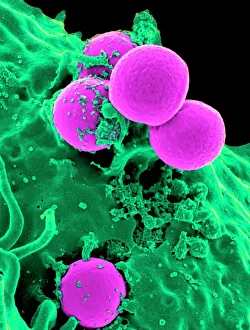
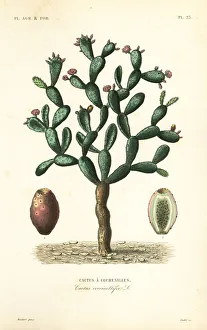
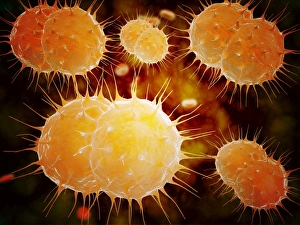
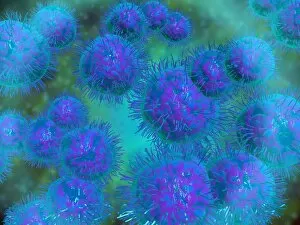
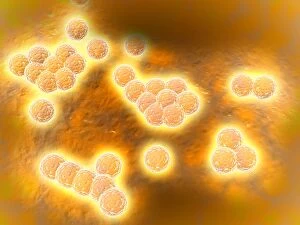
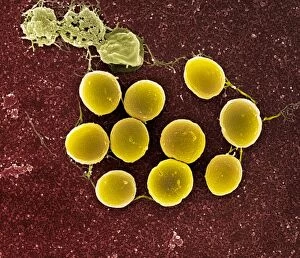
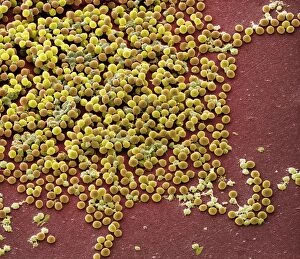
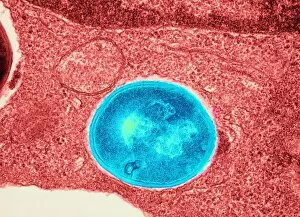
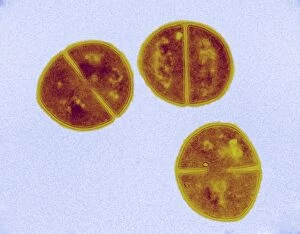
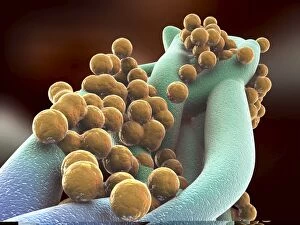
"Coccus: A Microscopic World Unveiled" In the realm of microbiology, coccus-shaped organisms have captivated scientists for centuries. From the captivating images of a neutrophil engulfing MRSA under SEM C018 / 8596 to the intricate details of cyanobacteria observed through SEM, these tiny entities continue to astound us. Gonorrhoea bacteria, as seen under TEM, remind us of the constant battle between humans and infectious diseases. Their resilient nature challenges our medical advancements and urges us to seek innovative solutions. Beyond their role in disease, coccus species also find themselves entwined with other living organisms. The cochineal beetle (Dactylopius coccus) delicately perches on plants like Nopalea cochenillifera and Kermes oak, leaving behind vibrant red pigments that have fascinated artists throughout history. The enchanting world of cochineal insects doesn't stop there; they form an intriguing relationship with domestic pigs and wild boars. These animals unknowingly become hosts for the beetles while roaming freely in their natural habitats. As we delve deeper into this microscopic universe, we encounter fascinating creatures such as brown soft scale (Coccus hesperidum), which thrives on leaves and contributes to ecological balance within its ecosystem. Even historical figures like Sir Percy Cox recognized the significance of these minuscule beings. His admiration is evident in Curtis British Entomology Plate 717—an exquisite engraving capturing the beauty and intricacy of a Cochineal Insect (Coccus cacti). Through scientific exploration aided by advanced imaging techniques, we uncover hidden wonders that exist beyond our naked eye's perception. Coccus species remind us that even in their smallness lies immense complexity—a testament to nature's ingenuity and resilience.