Chromosomes Collection (page 2)
Chromosomes are the intricate threads that hold the blueprint of life within our cells
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
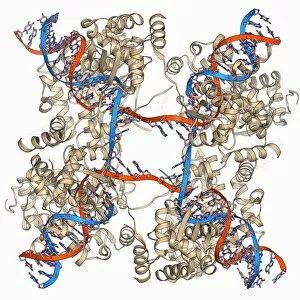
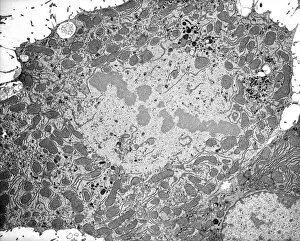
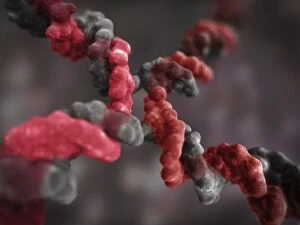
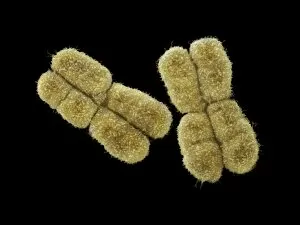
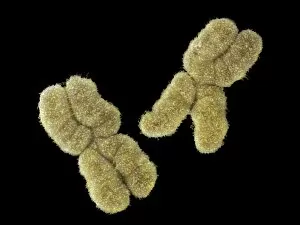
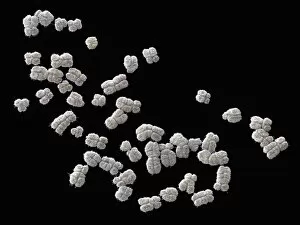
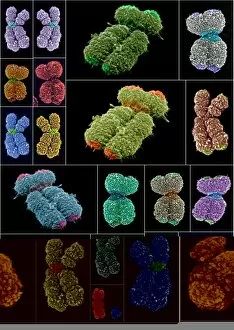
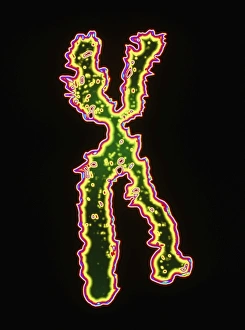
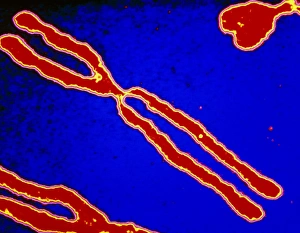
Chromosomes are the intricate threads that hold the blueprint of life within our cells. Among them, the X and Y chromosomes determine our biological sex, with males having one X and one Y chromosome. Through processes like mitosis, these chromosomes replicate themselves to ensure proper cell division. Under a light micrograph, we can witness this incredible phenomenon in action. In fluorescent micrographs capturing cell division, vibrant colors illuminate the intricate dance as they separate into two new cells. This mesmerizing display showcases the beauty hidden within our bodies. Examining a full set of male chromosomes under a scanning electron microscope (SEM) reveals their unique structure and arrangement. These microscopic images provide us with invaluable insights into our genetic makeup. Dividing cells captured in fluorescent micrographs remind us of the constant renewal happening inside us. Each split brings forth new possibilities for growth and development. Biomedical illustrations vividly depict DNA replication—a crucial process where bases attach to strands forming two identical double DNA strands. The twisting motion symbolizes how life's building blocks come together to create something extraordinary. A cross-sectional biomedical illustration unveils protein synthesis and ribosome activity—essential components for cellular function. This complex mechanism ensures that proteins are produced accurately according to instructions encoded in our chromosomes. The image of a single chromosome evokes wonder at its intricacy—an elegant structure carrying vital information that shapes who we are at a fundamental level. Astrocyte nerve cells intertwine with our understanding of chromosomes' role beyond reproduction—they play critical roles in brain function and communication between neurons. Under SEM imaging techniques, human chromosomes reveal their awe-inspiring complexity up close—each strand holding countless secrets waiting to be unraveled by scientists seeking answers about life itself.