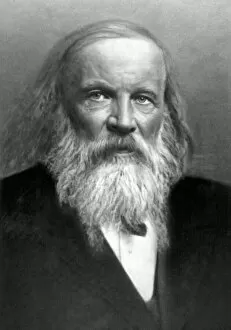Chemistry Collection
"Unveiling the Mysteries: A Journey through Chemistry's Timeline" Step back in time to 1869
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
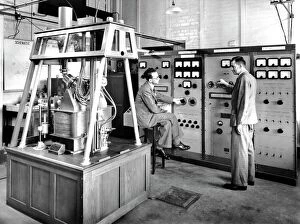
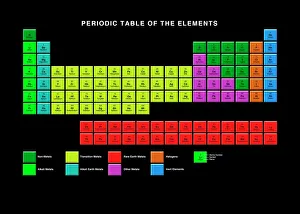
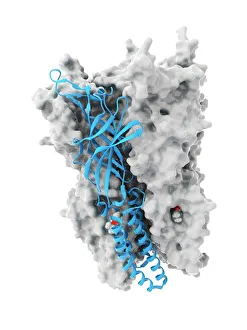
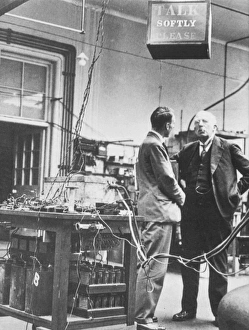
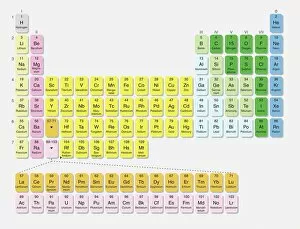
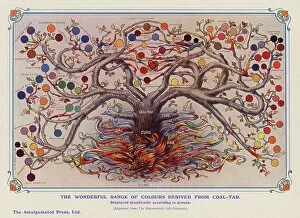
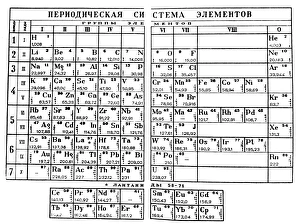
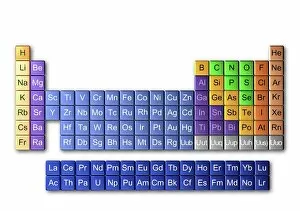
"Unveiling the Mysteries: A Journey through Chemistry's Timeline" Step back in time to 1869, when Dmitri Mendeleev introduced his groundbreaking creation - Mendeleyev's periodic table. This iconic masterpiece laid the foundation for understanding elements and their properties. Imagine holding a Bakelite telephone, marveling at its invention that revolutionized communication. It was during this era that chemistry began intertwining with everyday life, igniting curiosity and innovation. The mesmerizing dance of fire captivates our senses, reminding us of the transformative power of chemical reactions. From ancient alchemists like Count of St Germain to modern scientists like Dmitri Mendeleev, it has always been driven by those seeking knowledge and discovery. Colours derived from coal tar brought vibrant hues into our lives. Through colour lithography, we witnessed art merging with science as chemists unlocked the secrets hidden within nature's palette. Enter the realm of elements on the standard periodic table - a visual representation showcasing various element types and their unique characteristics. Copper and magnesium sulphate experiments (LM) exemplify how chemistry allows us to manipulate matter for practical purposes. In 1954, mass spectrometry emerged as a powerful tool enabling scientists to analyze complex substances at an atomic level. The birth of this technique marked another milestone in unraveling nature's mysteries. Chemistry not only impacts our physical world but also extends its reach into medicine. An anaesthetic inhibiting an ion channel C015/6718 showcases how chemicals can alter biological processes for therapeutic purposes. A laboratory clamp symbolizes precision and control in scientific experimentation – essential qualities that have propelled countless discoveries throughout history. Picture Ernest Rutherford standing tall amidst his research apparatus in Cavendish Laboratory – a testament to his pioneering work on atomic structure that reshaped our understanding of matter itself.