Cerebrovascular Accident Collection
"Cerebrovascular Accident: Unveiling the Intricacies of Stroke through Advanced Imaging Techniques" In the realm of medical diagnostics
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
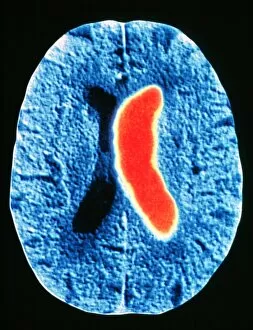
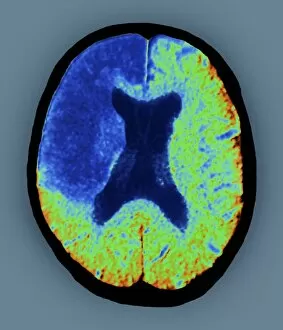
"Cerebrovascular Accident: Unveiling the Intricacies of Stroke through Advanced Imaging Techniques" In the realm of medical diagnostics, stroke remains a formidable adversary, affecting millions worldwide. However, with cutting-edge technologies such as MRI and 3D CT scans (C016/6419), we are gaining unprecedented insights into this cerebrovascular accident. Through intricate artwork depicting brain strokes (F008/0227), we witness the delicate interplay between life and its fragility. ECG traces intertwined with MRI brain scans reveal the complex nature of this condition, offering a visual representation that transcends words alone. Stroke's impact becomes palpable as these artistic renditions capture its essence - an unwelcome visitor disrupting neural pathways. The fusion of ECG traces and heads adorned by brains showcases how strokes disrupt our very core, leaving lasting imprints on both mind and body. With each stroke depicted in vivid detail through ECG traces and MRI brain scans, we unravel its enigmatic nature. These artworks serve as reminders that behind every diagnosis lies a unique story waiting to be told. CT scans emerge as powerful allies in our quest for understanding strokes' aftermaths. Their ability to visualize minute details allows us to comprehend the extent of damage inflicted upon fragile cerebral tissues. Stroke victims become more than just statistics; their struggles etched onto CT scan images that demand attention. As human heads intertwine with MRI and 3D CT scans, it becomes evident that stroke knows no boundaries - impacting lives regardless of age or background. These advanced imaging techniques enable us to navigate uncharted territories within our own minds while seeking answers to mitigate future risks. "Cerebrovascular Accident: Unveiling the Intricacies of Stroke through Advanced Imaging Techniques" sheds light on this silent assailant using captivating visuals derived from ECG traces, MRI scans, and 3D CT imagery.