Bacterial Collection
"Bacterial: Unveiling the Microscopic World of Disease and Discovery" Step into a time capsule as we journey through history, exploring the captivating realm of bacteria
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
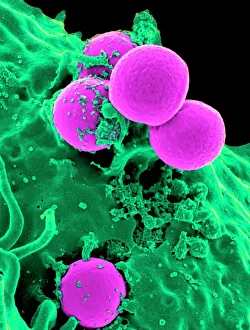
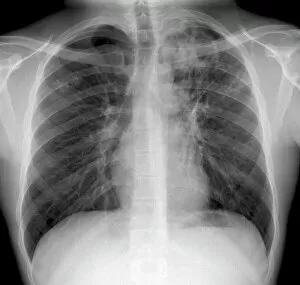
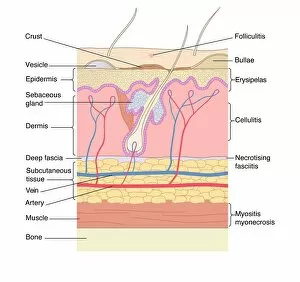
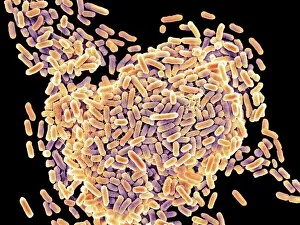
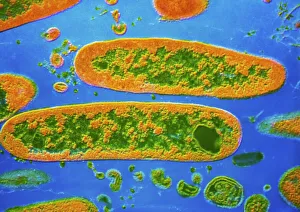
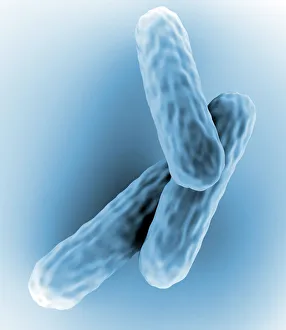
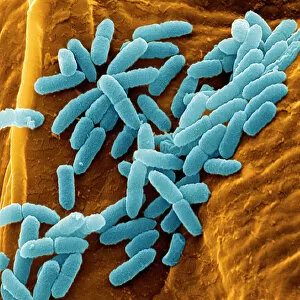
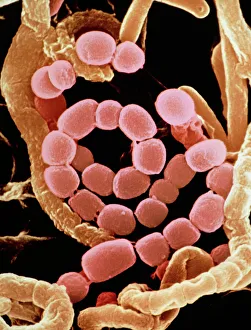
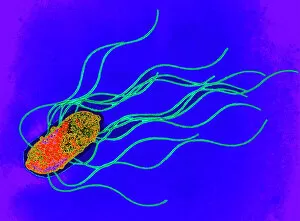
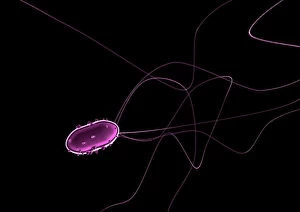
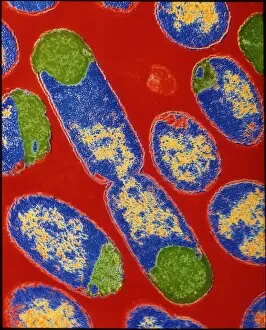
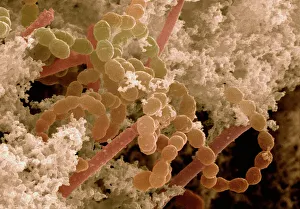
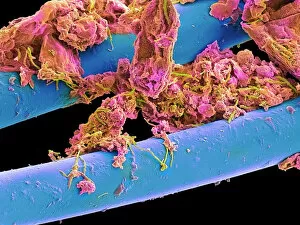
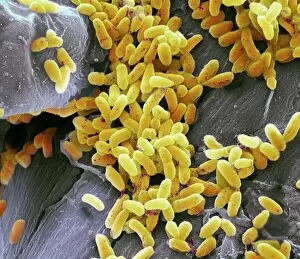
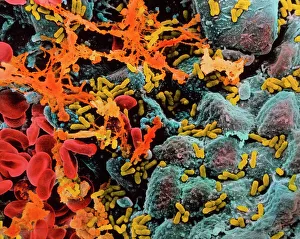
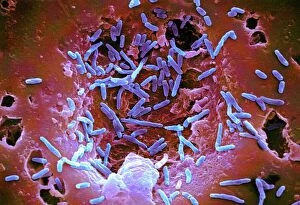
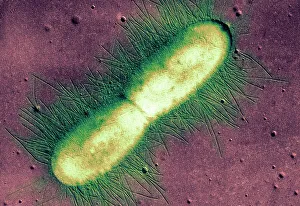
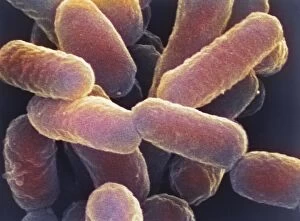
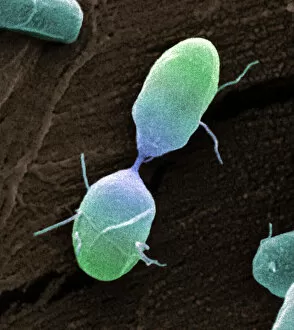
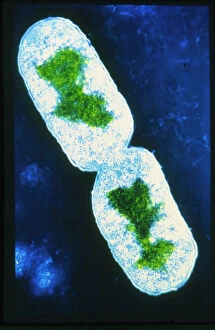
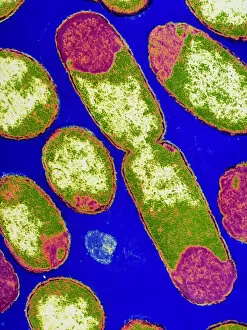
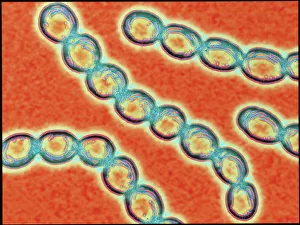
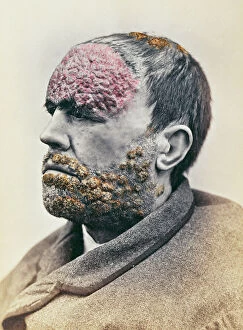
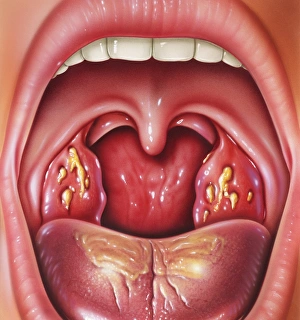
"Bacterial: Unveiling the Microscopic World of Disease and Discovery" Step into a time capsule as we journey through history, exploring the captivating realm of bacteria. From the haunting presence of plague doctors in 17th-century artwork to cutting-edge scientific images captured by scanning electron microscopes (SEM), prepare to be fascinated by these tiny yet formidable organisms. Witness the battle between our immune system and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) as a brave neutrophil engulfs it under SEM C018/8596. Marvel at the groundbreaking Calots spinal surgery from the 19th century, which revolutionized medical practices despite lurking bacterial threats. Peering through an X-ray, tuberculosis reveals its sinister grip on human lungs while skin disorders come alive in vivid artwork, reminding us of bacteria's impact on our bodies. E. coli bacteria, magnified under SEM, showcases their intricate structures that belie their harmful potential. Travel back to Soviet Russia in 1967 with a cholera vaccination poster that symbolizes humanity's fight against bacterial epidemics. Observe salmonella bacteria under SEM; their deceptively beautiful appearance belies their ability to cause severe illness. Delve into historical diagrams depicting anthrax cultures and learn about Yersinia pestis - responsible for devastating pandemics throughout history. The tuberculosis bacterium reminds us of its long-standing presence as one of humanity's greatest adversaries. Finally, witness nature's artistic flair with spiral spore chains formed by Streptomyces bacteria – showcasing both beauty and resilience within this microscopic world. Through these glimpses into bacterial realms past and present, we gain insight into our ongoing struggle against infectious diseases. Let this exploration ignite curiosity about microbial lifeforms that shape our existence – forever reminding us how knowledge can empower us in combating these invisible foes.