Axial Section Collection
"Exploring the Intricacies of the Human Brain: Axial Section Reveals Fascinating Insights" In the realm of medical imaging
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
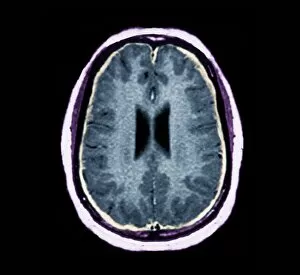
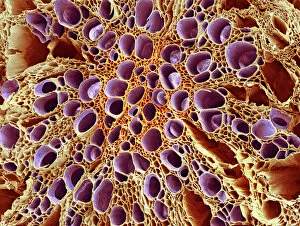
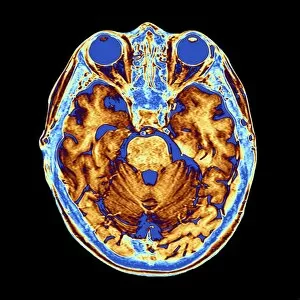
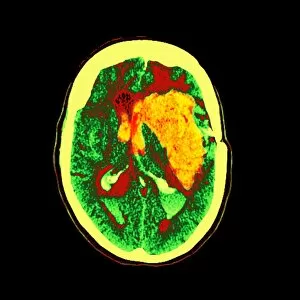
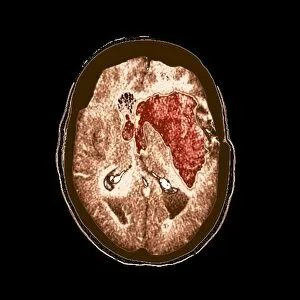
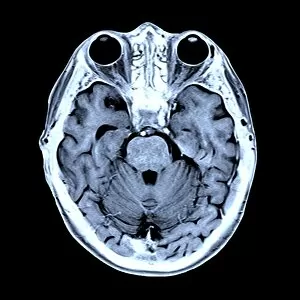
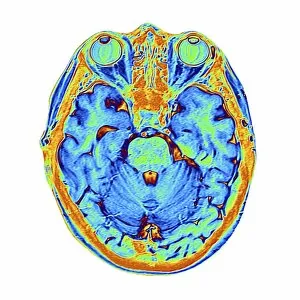
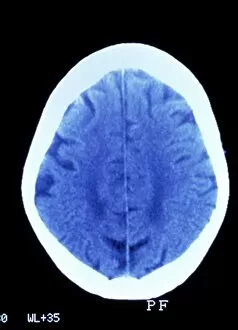
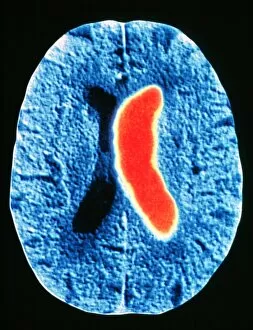
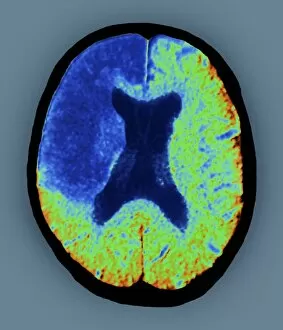
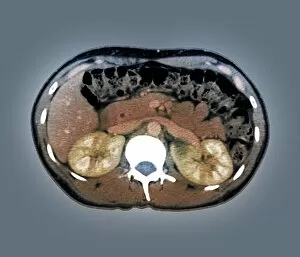
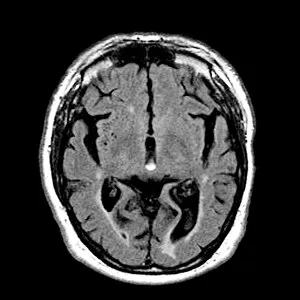
"Exploring the Intricacies of the Human Brain: Axial Section Reveals Fascinating Insights" In the realm of medical imaging, axial section scans provide a window into the complex workings of our most vital organ – the brain. From unraveling mysteries like bacterial meningitis to shedding light on conditions such as alcoholic dementia, these scans have revolutionized our understanding of neurological disorders. One remarkable application is seen in MRI scans that expose bacterial meningitis, allowing doctors to identify and treat this potentially life-threatening infection promptly. Similarly, MRI scans play a crucial role in diagnosing alcoholic dementia by revealing structural abnormalities within the brain. Delving deeper into neuroimaging techniques, SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) unveils intricate details about xylem tissue present in plants. This microscopic exploration helps scientists comprehend how water and nutrients are transported through plant structures. The power of MRI technology extends beyond infectious diseases and alcohol-related conditions. With images like "MRI brain scan F006 / 9208" or "Coloured MRI scan of the human head F007 / 4202, " we witness stunning visualizations that aid in detecting brain haemorrhages - critical events requiring immediate medical attention. Moreover, coloured MRI scans like "F007 / 4205" or "F006 / 9205" offer an artistic blend with scientific precision, showcasing both beauty and complexity within our own heads. These captivating visuals serve as valuable tools for researchers studying various aspects of brain function and pathology. Not limited to just MRIs, CT scans also contribute significantly to neurological diagnosis. In cases like stroke detection depicted by multiple "Stroke CT scan (s), " these imaging techniques enable swift identification and intervention for patients experiencing this sudden interruption in blood supply to their brains. As we continue exploring axial sections through advanced imaging technologies, we unlock new dimensions in neuroscience research and clinical practice alike.