Australopithecus Collection
"Australopithecus: Unveiling the Ancient Hominid Legacy" Step back in time and explore the fascinating world of Australopithecus
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
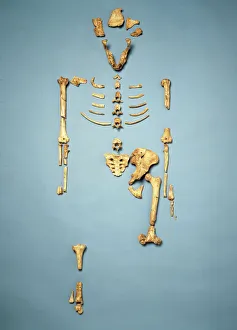
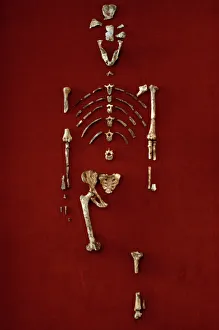
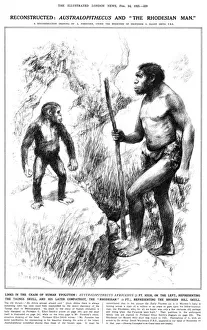
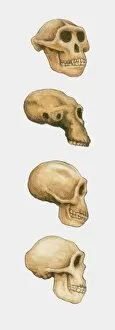
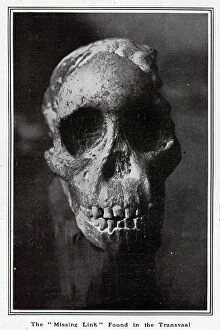
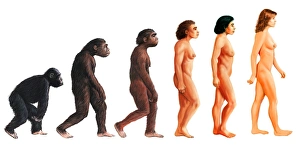
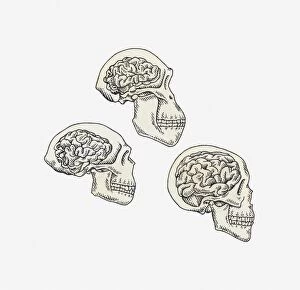
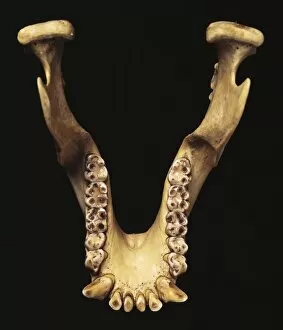
"Australopithecus: Unveiling the Ancient Hominid Legacy" Step back in time and explore the fascinating world of Australopithecus, a genus of hominids that once roamed our planet millions of years ago. From their crania to footprints, these remarkable creatures have left behind an intriguing trail for us to decipher. One iconic specimen is Australopithecus afarensis (AL 288-1), affectionately known as Lucy. This partial skeleton provided invaluable insights into our early ancestors' anatomy and locomotion. With her discovery, scientists gained a deeper understanding of how bipedalism evolved. It also shared the stage with another ancient human ancestor - Rhodesian Man. Together, they painted a vivid picture of our evolutionary journey, showcasing both similarities and differences between species. The Makapansgat Pebble further adds to this narrative by revealing early signs of symbolic thinking within Australopithecus communities. This small stone artifact suggests that these hominids possessed cognitive abilities beyond what was previously believed. Illustrations depicting the skulls of Australopithecus, Homo habilis, and Homo sapiens offer a visual representation of how our lineage has transformed over time. These comparisons highlight key anatomical changes that occurred during human evolution. Footprints preserved in volcanic ash provide yet another glimpse into the lives led by Australopithecus individuals like Lucy. These tracks reveal their walking patterns and social behaviors while leaving us awe-inspired at their existence so long ago. Mrs. Ples skull stands as one of South Africa's most significant fossil finds from this genus. Its discovery shed light on new aspects regarding brain size and cranial features among early hominids. Through meticulous reconstructions presented chronologically, we witness the gradual transformation from primitive forms to more advanced species within the Australopithecus lineage. Each step forward brings us closer to our modern human form.