Atom Collection
"Unveiling the Mysteries of the Atom: From Northern Lights to Quantum Leaps" In the ethereal dance of the Northern lights
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
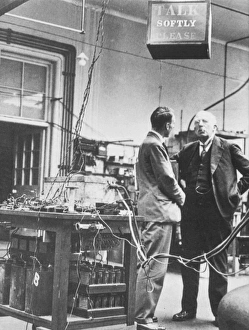
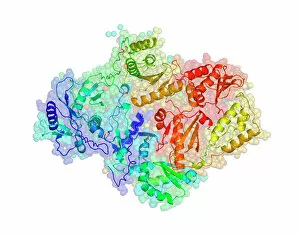
"Unveiling the Mysteries of the Atom: From Northern Lights to Quantum Leaps" In the ethereal dance of the Northern lights, nature showcases its own version of atomic beauty. Much like these mesmerizing lights, our understanding of atoms has evolved through groundbreaking scientific discoveries. One such milestone occurred in E. Rutherford's Cavendish Laboratory, where he unraveled the atom's structure and introduced us to its nucleus. This pivotal moment paved the way for Niels Bohr's caricatured quantum model, depicting electrons orbiting around a central core. The power within an atom is not limited to theory alone; it manifests itself in nuclear fission artwork that captures both its destructive force and potential energy release. Similarly, Britain's Ariel Atom embodies this dynamism with its sleek design and exhilarating speed. Delving deeper into atomic intricacies reveals Immunoglobulin G antibody molecule F007/9894 - a crucial defender against pathogens within our immune system. Its intricate structure mirrors the complexity hidden within every atom. Just as science progresses, so does technology - exemplified by Ariel Atom 500 and its cutting-edge engineering prowess. It pushes boundaries much like artists who depict atomic structures in captivating artworks or scientists who unveil quantized orbits resembling those found in celestial bodies' paths. Peering into helium atoms' electron structures unveils their unique properties while HIV reverse transcription enzyme sheds light on how viruses manipulate genetic material at an atomic level. Finally, we arrive at 2009 Ariel Atom - embodying innovation and evolution just as our understanding of atoms continues to expand exponentially. From enchanting natural phenomena like Northern lights to pioneering research conducted by brilliant minds like Rutherford and Bohr; from artistic interpretations capturing atomic wonders to technological marvels pushing limits – each hint represents a facet of humanity's ceaseless quest to unravel the enigmatic world of atoms.