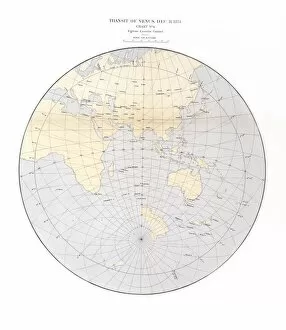
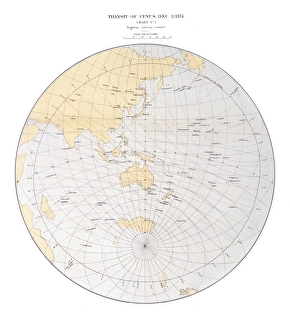
Astrophysics Collection (page 19)
Astrophysics, the captivating realm where science and wonder intertwine, unveils the secrets of our vast universe
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
Astrophysics, the captivating realm where science and wonder intertwine, unveils the secrets of our vast universe. From the iconic "Pale Blue Dot" image captured by Voyager 1 to the mesmerizing Hubble Ultra Deep Field 2012 photograph, astrophysics continues to expand our cosmic understanding. In 1919, during a solar eclipse, Sir Arthur Eddington's groundbreaking experiment confirmed Einstein's theory of general relativity. This pivotal moment paved the way for further astronomical breakthroughs. Gazing at Orion's Belt in awe, we are reminded of its celestial beauty and significance within our night sky. The Hubble Ultra Deep Field galaxies capture our imagination as they reveal countless distant galaxies scattered across space-time. The MAP microwave background survey provided us with an unprecedented glimpse into the early universe, uncovering ancient patterns imprinted on cosmic radiation. Meanwhile, the ethereal glow of the Orion Nebula showcases stellar birth in all its splendor. Amongst these wonders lies one of nature's most breathtaking creations: The Pillars of Creation. These colossal gas and dust structures within M16 remind us that even amidst chaos, beauty emerges. Delving deeper into nebulae like Sh 2-106 through stunning images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope leaves us awestruck by their intricate formations and vibrant colors. Witnessing gas pillars in the Eagle Nebula evokes a sense of both fragility and resilience found throughout space. Revisiting history once more brings us back to that transformative moment during a solar eclipse in 1919 when scientific theories were validated against nature itself. It was then that humanity took another step towards unraveling universal mysteries. Lastly, we encounter the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB), an echo from nearly fourteen billion years ago when light first permeated our expanding cosmos after the Big Bang. This faint radiation holds vital clues about our origins and paints a vivid picture of how everything began.