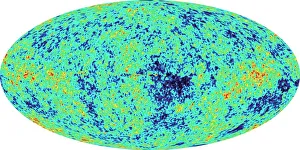
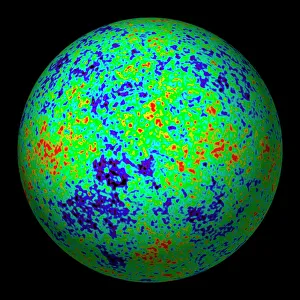
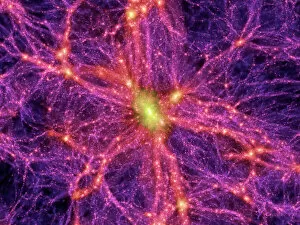
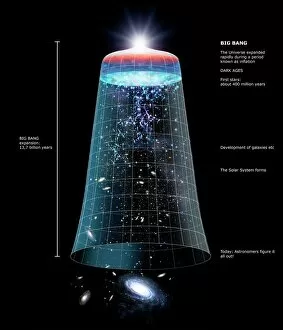
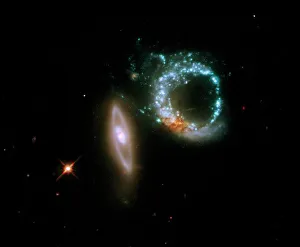Astrophysical Collection
Astrophysical wonders never cease to amaze us, reminding us of our infinitesimal place in the vastness of the universe
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
Astrophysical wonders never cease to amaze us, reminding us of our infinitesimal place in the vastness of the universe. Take a moment to ponder the significance of these celestial marvels. The iconic image known as "Pale Blue Dot" captured by Voyager 1 serves as a humbling reminder of Earth's minuscule size amidst the cosmic expanse. It reminds us that we are merely inhabitants on this tiny speck floating through space. In 2012, Hubble Ultra Deep Field unveiled an awe-inspiring snapshot showcasing thousands of galaxies, each containing billions of stars. This breathtaking view allows us to glimpse into the depths of time and witness the birth and death cycles occurring across countless light-years. The historic 1919 solar eclipse provided evidence supporting Einstein's theory of general relativity, forever changing our understanding of gravity and its effects on light bending around massive objects. Orion's Belt, a prominent feature in our night sky, guides stargazers towards Orion Nebula - a stellar nursery where new stars are born from swirling clouds of gas and dust. Its ethereal beauty captivates observers with its vibrant colors and intricate details. The Pillars of Creation within Eagle Nebula stand tall as colossal columns sculpted by stellar winds and intense radiation. These towering structures serve as incubators for new star formation, reminding us that even in seemingly desolate regions lies immense potential for life to emerge. Nebula Sh 2-106 presents itself like an otherworldly painting when observed through HST imagery. Its mesmerizing mixtures of gases create stunning hues that ignite curiosity about what lies beyond our own galaxy. Gas pillars within Eagle Nebula offer glimpses into cosmic nurseries where young stars form amidst turbulent surroundings. These majestic formations showcase nature's ability to shape matter into extraordinary shapes over millions or billions of years. Once again referencing the pivotal 1919 solar eclipse.