Adipose Tissue Collection
Adipose tissue, commonly known as fat cells, plays a crucial role in our bodies. These specialized cells are responsible for storing and releasing energy as needed
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
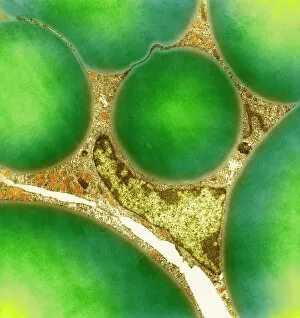
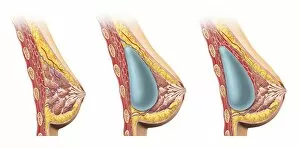
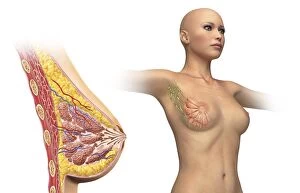
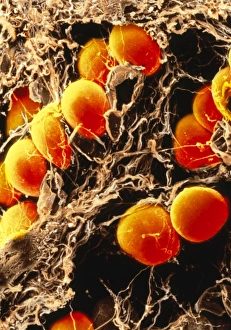
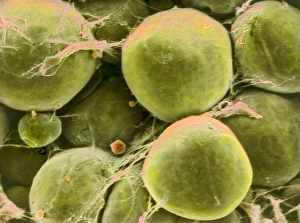
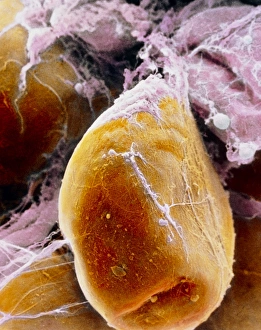
Adipose tissue, commonly known as fat cells, plays a crucial role in our bodies. These specialized cells are responsible for storing and releasing energy as needed. Under the microscope, through Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), we can observe their unique structure. When it comes to the female breast's anatomy, a significant component. Medical illustrations of the female breast showcase its composition and function. A cross-section of a woman's breast implant reveals how adipose tissue surrounds and supports these implants. In cutaway views of the female breast with lymphatic glands displayed, we can see how adipose tissue intertwines with these essential structures. It highlights the intricate relationship between fat cells and lymphatic drainage within this area. Further examination shows us a cross-section of a woman's torso with her breasts cut away, revealing the distribution throughout this region. This visual representation helps us understand its presence and contribution to body shape. Artwork depicting human fat cells gives us an artistic interpretation of their appearance under different conditions or magnifications - such as artwork F006/2275 and F006/2274. These visuals provide insight into their size, arrangement, and overall structure. Additionally, we find relevance in including an image of leptin molecules - hormones secreted by adipocytes that regulate appetite and metabolism (F006/9243). Understanding these molecules' role deepens our comprehension of how adipose tissue impacts various bodily functions beyond mere storage. Moreover, artwork showcasing fat tissues allows us to appreciate its complexity visually. The intricate network formed by blood vessels within this connective tissue becomes apparent through such depictions. Lastly, although not directly related to adipose tissue itself but worth mentioning due to its connection with digestion is artwork illustrating intestinal villi - finger-like projections lining our intestines that aid nutrient absorption (artwork). Exploring images ranging from TEM micrographs to medical illustrations provides valuable insights into adipose tissue's significance in the female breast and beyond.