Acid Rain Collection
The devastating effects of acid rain are evident in the limestone pavement above Malham Cove, where deep erosion has left behind clints and grykes
All Professionally Made to Order for Quick Shipping
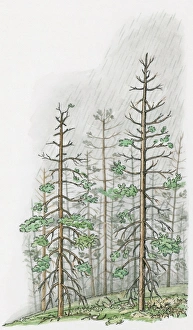
The devastating effects of acid rain are evident in the limestone pavement above Malham Cove, where deep erosion has left behind clints and grykes. These unique formations not only showcase the destructive power but also provide a crucial habitat for rare and unusual plants like hart's tongue ferns. As you traverse this landscape, you can't help but marvel at the intricate patterns created by well-developed clints and grykes, reminding us of nature's resilience even in the face of adversity. In an illustration depicting torrential acid rain damaging tall trees on a hill, we witness the alarming consequences of this environmental phenomenon. The image serves as a stark reminder that no ecosystem is immune to its detrimental effects. Even in bustling cities like Brussels, Belgium, acid rain leaves its mark on historic landmarks such as town halls, eroding their grandeur over time. Terracotta pots housing three plants tell a tale of contrasting health states caused by acid rain. One plant thrives while another struggles to survive under its corrosive influence. This visual representation highlights how some species adapt and withstand these harsh conditions while others succumb to their toxic embrace. The eruption artwork captures the explosive force unleashed when acidic precipitation interacts with natural elements. Just as volcanoes shape landscapes through eruptions, so too does acid rain reshape our environment through erosion and degradation. Even statues are not spared from the erosive power of acid rain; they stand weathered and worn as reminders of this ongoing battle against environmental degradation. Likewise, spruce leaves bear visible scars inflicted by acidic droplets—a poignant symbol illustrating how individual organisms suffer within larger ecosystems affected by this atmospheric pollution. Acid rain erosion continues to pose significant challenges worldwide—its impact felt across diverse terrains like limestone pavements or towering hillsides alike, and is imperative that we recognize our role in mitigating this issue through sustainable practices and collective action towards preserving our planet's delicate balance before irreversible damage is done.